Class 5: Maths Chapter 5 solutions. Complete Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Notes.
Contents
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 5-Maths (Problem Set 18) – Part 1: Chapter 5- Fractions
Maharashtra Board 5th Maths Chapter 5, Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 solutions
Important Questions and Answers.
Convert the given fractions into like fractions.![]()
Solution :
8 is the multiple of 4 So, make 8, the common denominator 34=3×24×2=68.Thus 6/8 and 5/8are the required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
The number 35 is a multiple of both 5 and 7 So, making 35 as the common denominater 35=3×75×7=2135,37=3×57×5=1535 Therefore, 21/35 and 15/35 are required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
Here 10 is the multiples of 5. So make 10 as the common denominator 45=4×25×2=810. Thus 8/10 and 3/10 are required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
Least common multiple of 9 and 6 is 18. So, make, 18 as the common denominator. 29=2×29×2=418,16=1×36×3=318. Thus, 4/18 and 3/18 are the required like fractions.

Solution :
Least common multiple of 4 and 3 is 12 So, make 12 as common denominator 14=1×34×3=312,23=2×43×4=812. so, 312,812 are required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
Least common multiple of 6 and 5 is 30 So, make 30 as common denominator 56=5×56×5=2530,45=4×65×6=2430 So, 2530,2430 are required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
Least common multiple of 8 and 6 is 24 So, make 24 as common denominator 38=3×38×3=924,16=1×46×4=424 So, 924,424 are required like fractions.
![]()
Solution :
Least common multiple of 6 and 9 is 18 So, make 18 as common denominator 16=1×36×3=318,49=4×29×2=818 So, 3/18 and 8/18 are the required like fractions.
Comparing like fractions
Example (1) A strip was divided into 5 equal parts. It means that each part is 1/5 . The coloured part is 35=15+15+15.![]()
The white part is 25=15+15. The coloured part is bigger than the white part. This tells us that 3/5 is greater than 2/5. This is written as 3/5 > 2/5.
Example (2) This strip is divided into 8 equal parts. 3 of the parts have one colour and 4 have another colour. Here, 3/8 < 8/4.![]()
In like fractions, the fraction with the greater numerator is the greater fraction.
Comparing fractions with equal numerators
You have learnt that the value of fractions with numerator 1 decreases as the denominator increases.
Even if the numerator is not 1, the same rule applies so long as all the fractions have a common numerator. For example, look at the figures below. All the strips in the figure are alike.
2 of the 3 equal parts of the strip ![]()
2 of the 4 equal parts of the strip 
2 of the 5 equal parts of the strip 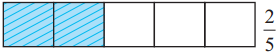
The figure shows that 2/3 > 2/4 > 5/2.
Of two fractions with equal numerators, the fraction with the greater denominator is the smaller fraction.
Comparing unlike fractions
Teacher : Suppose we have to compare the unlike fractions 3/5 and 4/7. Let us take an example to see how this is done. These two boys are standing on two blocks. How do we decide who is taller?
Sonu : But the height of the blocks is not the same. If both blocks are of the same height, it is easy to tell who is taller.
Nandu : Now that they are on blocks of equal height, we see that the boy on the right is taller.
Teacher : The height of the boys can be compared when they stand at the same height. Similarly, if fractions have the same denominators, their numerators decide which fraction is bigger.
Nandu : Got it! Let’s obtain the same denominators for both fractions.
Sonu : 5 × 7 can be divided by both 5 and 7. So, 35 can be the common denominator.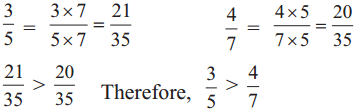
To compare unlike fractions, we convert them into their equivalent fractions so that their denominators are the same.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
59,1736
Solution :
36 is the multiple of 9 So, make 36 the common denominator 59=5×49×4=2036, Thus 20/36 and 17/36 are the required like fractions.
Question 2.
56,79
Solution:
Least common multiple of 6 and 9 is 18 So, make 18 as the common denominator 56=5×36×3=1518,79=7×29×2=1418 So, 15/18 and 14/18 are the required like fractions.
Question 3.
711,35
Solution:
Least common multiple of 11 and 5 is 55 So, make 55 as the common denominator. 711=7×511×5=3555,35=3×115×11=3355. Thus 35/55 and 33/55 are required like fractions.
Download PDF
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 5-Maths (Problem Set 18) – Part 1: Chapter 5- Fractions
Chapterwise Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 5 Maths :
Part 1
- Chapter 1- Roman Numerals (Problem Set 1)
- Chapter 2- Number Work (Problem Set 2)
- Chapter 2- Number Work (Problem Set 3)
- Chapter 2- Number Work (Problem Set 4)
- Chapter 2- Number Work (Problem Set 5)
- Chapter 2- Number Work (Problem Set 6)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 7)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 8)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 9)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 10)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 11)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 12)
- Chapter 3- Addition and Subtraction (Problem Set 13)
- Chapter 4- Multiplication and Division (Problem Set 14)
- Chapter 4- Multiplication and Division (Problem Set 15)
- Chapter 4- Multiplication and Division (Problem Set 16)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 17)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 18)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 19)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 20)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 21)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 22)
- Chapter 5- Fractions (Problem Set 23)
- Chapter 6- Angles (Problem Set 24)
- Chapter 6- Angles (Problem Set 25)
- Chapter 6- Angles (Problem Set 26)
- Chapter 6- Angles (Problem Set 27)
- Chapter 7- Circles (Problem Set 28)
- Chapter 7- Circles (Problem Set 29)
- Chapter 7- Circles (Problem Set 30)
- Chapter 7- Circles (Problem Set 31)
Part 2.
- Chapter 8- Multiples and Factors (Problem Set 32)
- Chapter 8- Multiples and Factors (Problem Set 33)
- Chapter 8- Multiples and Factors (Problem Set 34)
- Chapter 8- Multiples and Factors (Problem Set 35)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 36)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 37)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 38)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 39)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 40)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 41)
- Chapter 9- Decimal Fractions (Problem Set 42)
- Chapter 10- Measuring Time (Problem Set 43)
- Chapter 10- Measuring Time (Problem Set 44)
- Chapter 10- Measuring Time (Problem Set 45)
- Chapter 11- Problems on Measurement (Problem Set 46)
- Chapter 11- Problems on Measurement (Problem Set 47)
- Chapter 12- Perimeter and Area (Problem Set 48)
- Chapter 12- Perimeter and Area (Problem Set 49)
- Chapter 12- Perimeter and Area (Problem Set 50)
- Chapter 13- Three Dimensional Objects and Nets (Problem Set 51)
- Chapter 14- Pictographs (Problem Set 52)
- Chapter 15- Patterns (Problem Set 53)
- Chapter 16- Preparation for Algebra (Problem Set 54)
- Chapter 16- Preparation for Algebra (Problem Set 55)
- Chapter 16- Preparation for Algebra (Problem Set 56)
FAQs
You can download the Maharashtra State Board Books from the eBalbharti official website, i.e. cart.ebalbharati.in or from this article.
Students can get the Maharashtra Books for primary, secondary, and senior secondary classes from here. You can view or download the Maharashtra State Board Books from this page or from the official website for free of cost. Students can follow the detailed steps below to visit the official website and download the e-books for all subjects or a specific subject in different mediums.
Step 1: Visit the official website ebalbharati.in
Step 2: On the top of the screen, select “Download PDF textbooks”
Step 3: From the “Classes” section, select your class.
Step 4: From “Medium”, select the medium suitable to you.
Step 5: All Maharashtra board books for your class will now be displayed on the right side.
Step 6: Click on the “Download” option to download the PDF book.
As of now, the MSCERT and Balbharti are responsible for the syllabus and textbooks of Classes 1 to 8, while Classes 9 and 10 are under the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE).
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education, conducts the HSC and SSC Examinations in the state of Maharashtra through its nine Divisional Boards located at Pune, Mumbai, Aurangabad, Nasik, Kolhapur, Amravati, Latur, Nagpur and Ratnagiri.
About Maharashtra State Board (MSBSHSE)
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education or MSBSHSE (Marathi: महाराष्ट्र राज्य माध्यमिक आणि उच्च माध्यमिक शिक्षण मंडळ), is an autonomous and statutory body established in 1965. The board was amended in the year 1977 under the provisions of the Maharashtra Act No. 41 of 1965.
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE), Pune is an independent body of the Maharashtra Government. There are more than 1.4 million students that appear in the examination every year. The Maha State Board conducts the board examination twice a year. This board conducts the examination for SSC and HSC.
The Maharashtra government established the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, also commonly referred to as Ebalbharati, in 1967 to take up the responsibility of providing quality textbooks to students from all classes studying under the Maharashtra State Board. MSBHSE prepares and updates the curriculum to provide holistic development for students. It is designed to tackle the difficulty in understanding the concepts with simple language with simple illustrations. Every year around 10 lakh students are enrolled in schools that are affiliated with the Maharashtra State Board.
