Class 11: Physics Chapter 6 solutions. Complete Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 Notes.
Contents
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 11-Physics: Chapter 6- Mechanical Properties of Solids
Class 11: Physics Chapter 6 solutions. Complete Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 Notes.
1. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Change in dimensions is known as …………..
(A) deformation
(B) formation
(C) contraction
(D) strain.
Answer:
(A) deformation
Question 2.
The point on stress-strain curve at which strain begins to increase even without increase in stress is called…………
(A) elastic point
(B) yield point
(C) breaking point
(D) neck point
Answer:
(B) yield point
Question 3.
Strain energy of a stretched wire is 18 × 10-3 J and strain energy per unit volume of the same wire and same cross section is 6 × 10-3 J/m3. Its volume will be………….
(A) 3cm3
(B) 3 m3
(C) 6 m3
(D) 6 cm3
Answer:
(B) 3 m3
Question 4.
……………. is the property of a material which enables it to resist plastic deformation.
(A) elasticity
(B) plasticity
(C) hardness
(D) ductility
Answer:
(C) hardness
Question 5.
The ability of a material to resist fracturing when a force is applied to it, is called……………
(A) toughness
(B) hardness
(C) elasticity
(D) plasticity.
Answer:
(A) toughness
2. Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
Define elasticity.
Answer:
If a body regains its original shape and size after removal of the deforming force, it is called an elastic body and the property is called elasticity.
Question 2.
What do you mean by deformation?
Answer:
The change in shape or size or both of u body due to an external force is called deformation.
Question 3.
State the SI unit and dimensions of stress.
Answer:
- SI unit: N m-2 or pascal (Pa)
- Dimensions: [L-1M1T-2]
Question 4.
Define strain.
Answer:
Strain:
- Strain is defined as the ratio of change in dimensions of the body to its original dimensions.
Strain = change in dimensions original dimensions - Types of strain:
- Longitudinal strain,
- Volume strain,
- Shearing strain.
Question 5.
What is Young’s modulus of a rigid body?
Answer:
Young’s modulus (Y): It is the modulus of elasticity related to change in length of an object like a metal wire, rod, beam, etc., due to the applied deforming force.
Question 6.
Why bridges are unsafe after a very long use?
Answer:
A bridge during its use undergoes recurring stress depending upon the movement of vehicles on it. When bridge is used for long time, it loses its elastic strength and ultimately may collapse. Hence, the bridges are declared unsafe after long use.
Question 7.
How should be a force applied on a body to produce shearing stress?
Answer:
A tangential force which is parallel to the top and the bottom surface of the body should be applied to produce shearing stress.
Question 8.
State the conditions under which Hooke’s law holds good.
Answer:
Hooke’s Taw holds good only when a wire/body is loaded within its elastic limit.
Question 9.
Define Poisson’s ratio.
Answer:
Within elastic limit, the ratio of lateral strain to the linear strain is called the Poisson‘s ratio.
Question 10.
What is an elastomer?
Answer:
A material that can be elastically stretched to a larger value of strain is called an elastomer.
Question 11.
What do you mean by elastic hysteresis?
Answer:
- In case of some materials like vulcanized rubber, when the stress applied on a body decreases to zero, the strain does not return to zero immediately. The strain lags behind the stress. This lagging of strain behind the stress is called elastic hysteresis.
- Below figure shows the stress-strain curve for increasing and decreasing load. It encloses a loop. Area of loop gives the energy dissipated during deformation of a material.
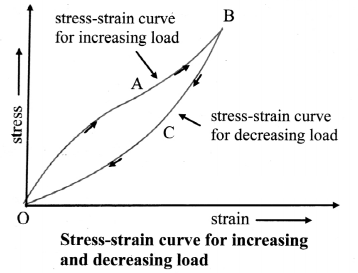
Question 12.
State the names of the hardest material and the softest material.
Answer:
Hardest material: Diamond
Softest material: Aluminium
[Note: Material with highest strength is steel whereas material with lowest strength is plasticine clay.]
Question 13.
Define friction.
Answer:
The property which resists the relative motion between two surfaces in contact is called friction.
Question 14.
Why force of static friction is known as ‘self-adjusting force?
Answer:
The force of static friction varies in accordance with applied force. Hence, it is called as self adjusting force.
Question 15.
Name two factors on which the coefficient of friction depends.
Answer:
Coefficient of friction depends upon:
- the materials of the surfaces in contact.
- the nature of the surfaces.
3. Answer in short:
Question 1.
Distinguish between elasticity and plasticity.
Answer:
| No. | Elasticity | Plasticity |
| i. | Body regains its original shape or size after removal of deforming force. | Body does not regain its original shape or size after removal of deforming force. |
| ii. | Restoring forces are strong enough to bring the displaced molecules to their original positions. | Restoring forces are not strong enough to bring the molecules back to their original positions. |
| Examples of elastic materials: metals, rubber, quartz, etc | Examples of plastic materials: clay, putty, plasticine, thick mud, etc |
Question 2.
State any four methods to reduce friction.
Answer:
Friction can be reduced by using polished surfaces, using lubricants, using grease and using ball bearings.
Question 3.
What is rolling friction? How does it arise?
Answer:
- Friction between two bodies in contact when one body is rolling over the other, is called rolling friction.
- Rolling friction arises as the point of contact of the body with the surface keep changing continuously.
Question 4.
Explain how lubricants help in reducing friction?
Answer:
- The friction between lubricant to surface is much less than the friction between two same surfaces. Hence using lubricants reduces the friction between the two surfaces.
- When lubricant is applied to machine parts, it fills the depression present on the surface in contact. Thus, less friction is occurred between machine parts.
- Application of lubricants also reduces wear and tear of machine parts which in turn reduces friction.
- Advantage: Reduction in function reduces dissipation of energy in machines due to which efficiency of machines increases.
Question 5.
State the laws of static friction.
Answer:
Laws of static friction:
- First law: The limiting force of static friction (FL) is directly proportional to the normal reaction (N) between the two surfaces in contact.
FL ∝ N
∴ FL = µs N
where, µs = constant called coefficient of static friction. - Second law: The limiting force of friction is
independent of the apparent area between the surfaces in contact, so long as the normal reaction remains the same. - Third law: The limiting force of friction depends upon materials in contact and the nature of their surfaces.
Question 6.
State the laws of kinetic friction.
Answer:
Laws of kinetic friction:
- First law: The force of kinetic friction (Fk) is directly proportional to the normal reaction (N) between two surfaces in contact.
Fk ∝ N
∴ Fk = µkN
where, µk = constant called coefficient of kinetic friction. - Second law: Force of kinetic friction is independent of shape and apparent area of the surfaces in contact.
- Third law: Force of kinetic friction depends upon the nature and material of the surfaces in contact.
- Fourth law: The magnitude of the force of kinetic friction is independent of the relative velocity between the object and the surface provided that the relative velocity is neither too large nor too small.
Question 7.
State advantages of friction.
Answer:
Advantages of friction:
- We can walk due to friction between ground and feet.
- We can hold object in hand due to static friction.
- Brakes of vehicles work due to friction; hence we can reduce speed or stop vehicles.
- Climbing on a tree is possible due to friction.
Question 8.
State disadvantages of friction.
Answer:
Disadvantages of friction:
- Friction opposes motion.
- Friction produces heat in different parts of machines. It also produces noise.
- Automobile engines consume more fuel due to friction.
Question 9.
What do you mean by a brittle substance? Give any two examples.
Answer:
- Substances which breaks within the elastic limit are called brittle substances.
- Examples: Glass, ceramics.
4. Long answer type questions:
Question 1.
Distinguish between Young’s modulus, bulk modulus and modulus of rigidity.
Answer:


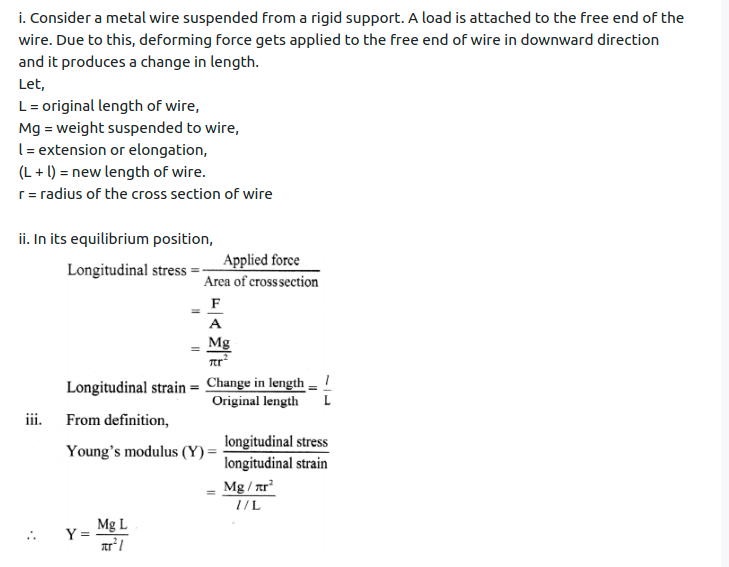










Download PDF
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 11-Physics: Chapter 6- Mechanical Properties of Solids
Chapterwise Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 11 Physics :
- Chapter 1- Units and Measurements
- Chapter 2- Mathematical Methods
- Chapter 3- Motion in a Plane
- Chapter 4- Laws of Motion
- Chapter 5- Gravitation
- Chapter 6- Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Chapter 7- Thermal Properties of Matter
- Chapter 8- Sound
- Chapter 9- Optics
- Chapter 10- Electrostatics
- Chapter 11- Electric Current Through Conductors
- Chapter 12- Magnetism
- Chapter 13- Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System
- Chapter 14- Semiconductors
FAQs
You can download the Maharashtra State Board Books from the eBalbharti official website, i.e. cart.ebalbharati.in or from this article.
Students can get the Maharashtra Books for primary, secondary, and senior secondary classes from here. You can view or download the Maharashtra State Board Books from this page or from the official website for free of cost. Students can follow the detailed steps below to visit the official website and download the e-books for all subjects or a specific subject in different mediums.
Step 1: Visit the official website ebalbharati.in
Step 2: On the top of the screen, select “Download PDF textbooks”
Step 3: From the “Classes” section, select your class.
Step 4: From “Medium”, select the medium suitable to you.
Step 5: All Maharashtra board books for your class will now be displayed on the right side.
Step 6: Click on the “Download” option to download the PDF book.
As of now, the MSCERT and Balbharti are responsible for the syllabus and textbooks of Classes 1 to 8, while Classes 9 and 10 are under the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE).
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education, conducts the HSC and SSC Examinations in the state of Maharashtra through its nine Divisional Boards located at Pune, Mumbai, Aurangabad, Nasik, Kolhapur, Amravati, Latur, Nagpur and Ratnagiri.
About Maharashtra State Board (MSBSHSE)
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education or MSBSHSE (Marathi: महाराष्ट्र राज्य माध्यमिक आणि उच्च माध्यमिक शिक्षण मंडळ), is an autonomous and statutory body established in 1965. The board was amended in the year 1977 under the provisions of the Maharashtra Act No. 41 of 1965.
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE), Pune is an independent body of the Maharashtra Government. There are more than 1.4 million students that appear in the examination every year. The Maha State Board conducts the board examination twice a year. This board conducts the examination for SSC and HSC.
The Maharashtra government established the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, also commonly referred to as Ebalbharati, in 1967 to take up the responsibility of providing quality textbooks to students from all classes studying under the Maharashtra State Board. MSBHSE prepares and updates the curriculum to provide holistic development for students. It is designed to tackle the difficulty in understanding the concepts with simple language with simple illustrations. Every year around 10 lakh students are enrolled in schools that are affiliated with the Maharashtra State Board.
Read More
IndCareer Board Book Solutions App
IndCareer Board Book App provides complete study materials for students from classes 1 to 12 of Board. The App contains complete solutions of NCERT books, notes, and other important materials for students. Download the IndCareer Board Book Solutions now.

