Class 6: Maths Chapter 5 solutions. Complete Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Notes.
Contents
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5–Fractions
RS Aggarwal 6th Maths Chapter 5, Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 solutions
Ex 5A Solutions
Question 1.
Solution:
(i) 34
(ii) 14
(iii) 23
(iv) 310
(v) 49
(vi) 38
Question 2.
Solution:
In the figure, 49 is shaded
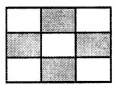
Question 3.
Solution:
In the figure, whole rectangle is not divided into four equal parts.
Question 4.
Solution:
(i) Three-fourths = 34
(ii) Four-sevenths = 47
(iii) Two-fifths = 25
(iv) Three-tenths = 310
(v) One-eighth = 18
(vi) three-tenths = 56
(vii) five-sixths = 89
(vii) seven-twelfths = 712
Question 5.
Solution:
(i) In 49, numerator is 4 and denominator is 9.
(ii) In 611, numerator is 6 and denominator is 11.
(iii) In 815, numerator is 8 and denominator is 15.
(iv) In 1217, numerator is 12 and denominator is 17.
(v) 51 , numerator is 5 and denominator is 1.
Question 6.
Solution:
(z) Numerator = 3, Denominator = 8, then fraction = 38.
(ii) Numerator = 5, Denominator = 12, then fraction = 512
(iii) Numerator = 7, Denominator = 16, then fraction = 716.
(iv) Numerator = 8, Denominator = 15, then fraction = 815
Question 7.
Solution:
(i) 23 = two-thirds
(ii) 49 = four-ninths
(iii) 25 = two-fifths
(iv) 710 = seven-tenths
(v) 13 = one-thirds
(vi) 34 = three-fourth
(vii) 38 = three-eighths
(viii) 914 = nine-fourteenths
(ix) 511 = five-elevanths
(x) 615 = six-fifteenths
Question 8.
Solution:
24 minutes is the fraction of 1 hour i.e.,
60 minutes = 2460
Question 9.
Solution:
Natural number between 2 to 10 are 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 = 9
Out of these prime number are 2, 3, 5, 7 = 4
Fraction = 49
Question 10.
Solution:
(i) 23 of 15 pens = 23 x 15 = 2 x 5 = 10 pens.
(ii) 23 of 27 balls = 23 x 27 = 2 x 9 = 18 balls.
(iii) 23 of 36 balloons = 23 x 36 = 2 x 12 = 24 balloons. Ans.
Question 11.
Solution:
(i) 34 of 16 cups = 34 x 16 = 3 x 4
= 12 cups.
(ii) 34 of 28 rackets = 34 x 28 = 3 x 7
= 21 rackets.
(iii) 34 of 32 books = 34 x 32 = 3 x 8
= 24 books. Ans.
Question 12.
Solution:
Total number of pencils Neelam has = 25
No. of pencils given to Meena
= 45 of 25
= 45 x 25 – 20
No. of pencils left with Neelam = 25 – 20 = 5
Question 13.
Solution:
(i) 38
Take a line segment OA = one unit of length
Divide it into 8 equal parts and take 3 parts at P, then P represents 38.
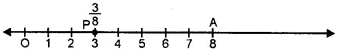
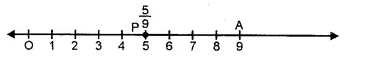
(ii) 59
(a) Take a line segment OA = one unit of length.
(b) Divide it into nine equal parts and take 5 parts at P, then P represents 59.
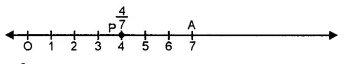
(iii) 47
(a) Take a line segment OA = one unit of length.
(b) Divide it into 7 equal parts and take 4 parts at P then P represents 47.
(iv) 25
(a) Take a line segment OA = 1 unit of length.
(b) Divide it with 5 equal parts and take 2 parts and P then P represents 25.

(v) 14
(a) Take a line segment OA = 1 unit of length.
(b) Divide it with 4 equal parts and take 1 parts and P then P represents 14.

Ex 5B Solutions
Question 1.
Solution:
We know that, a fraction is proper if its denominator is greater than its numerator. Therefore,
12, 35 and 1011 are proper fractions. Ans.
Question 2.
Solution:
We know that a fraction is improper if its denominator is less than its numerator
Therefore,

are improper fractions. Ans.
Question 3.
Solution:
Six improper fractions with denominator 5 can be
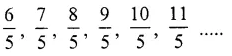
Question 4.
Solution:
Six improper fraction with denominator 13 can be

Question 5.
Solution:
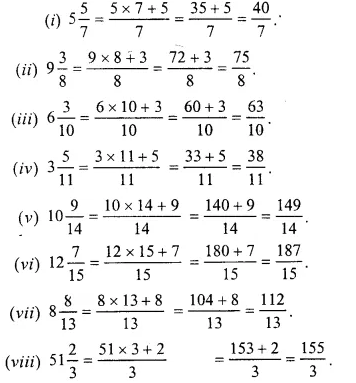
Question 6.
Solution:

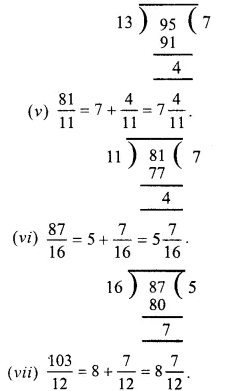

Question 7.
Solution:
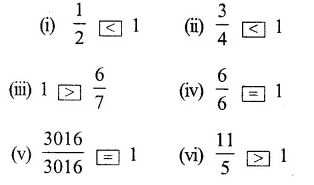
Question 8.
Solution:
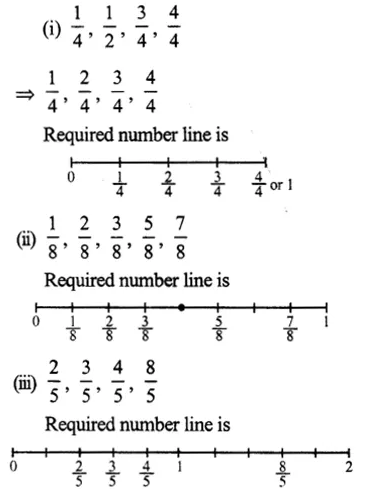
Ex 5C Solutions
Question 1.
Solution:
(i) 23
= 2X23X2
= 46
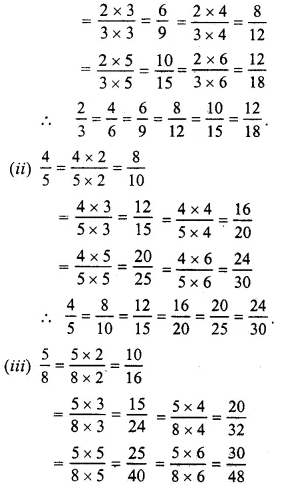
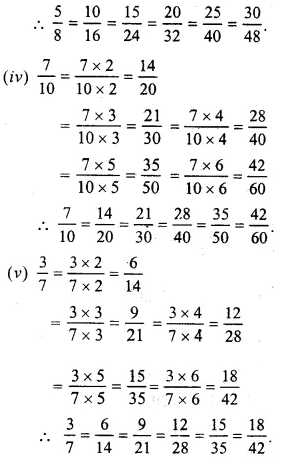
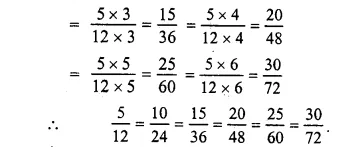
Question 2.
Solution:
(i) In 56 and 2024
56 = 2024

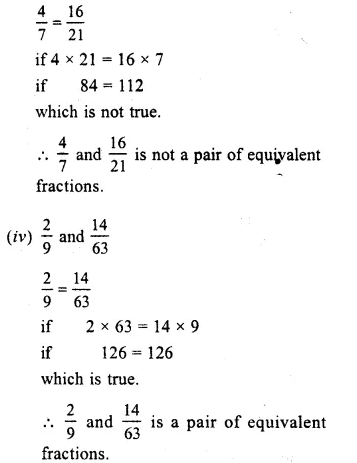
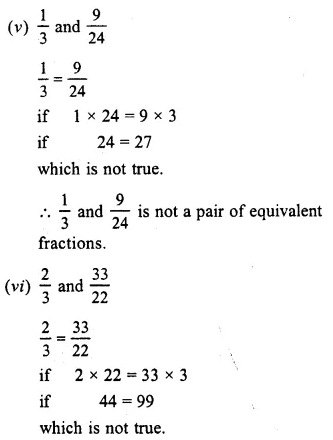

Question 3.
Solution:
Equivalent fraction of 35 having
(i) Denominator = 30 and 30 = 5 x 6
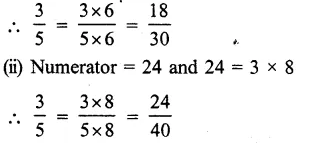
Question 4.
Solution:
(i) Denominator = 54, and 54 = 9 x 6

Question 5.
Solution:
Equivalent fraction of 611 having
(i) Denominator = 77 and 77 = 11 = 7
611
= 6X711X7
= 4277
(ii) Numerator = 60 and 60 = 6 x 10
611
= 6X1011X10
= 60110
Question 6.
Solution:
Let 2430 = 4x
In order to get 4, divide 24 by 6,

Question 7.
Solution:
Equivalent fraction of 3648, with
(i) Numerator 9 and 9 = 36 + 4
3648=36÷448÷4=912
(ii) Denominator = 4 and 4 = 48 ÷ 12
3648=36÷1248÷12=34
Question 8.
Solution:
Equivalent fraction of 5670 with
(i) Numerator 4 and = 56 ÷ 14
5670=56÷1470÷14=45
(ii) Denominator =10 and 10 = 70 ÷ 7
5670=56÷770÷7=810
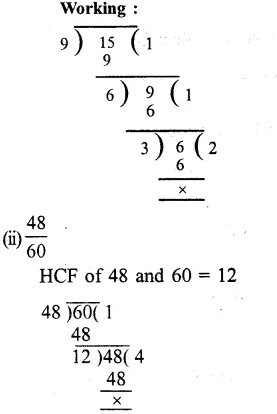
Question 9.
Solution:
(i) In 915, HCF of 9 and 15 = 3
Now, dividing each term by 3, we get:
915=9÷315÷3=35
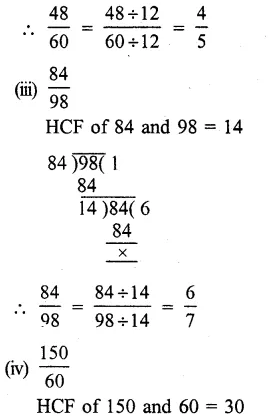

Question 10.
Solution:
We know that a fraction is in its simplest form if its HCF of numerator and denominator is 1.


Question 11.
Solution:
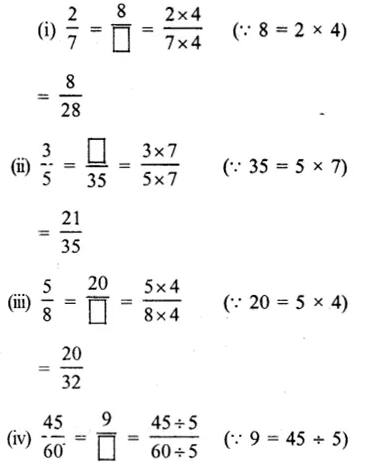

Ex 5D Solutions
Question 1.
Solution:
(i) Like fraction : Fractions having the same denominators are called like fractions. For examples:
211,311,411,511,811
(ii) Unlike fraction : Fraction having the different denominators, are called unlike fractions. For examples:
13,47,59,38,711
Question 2.
Solution:
We know that like fractions have same denominator
Now 35,710,815,1130
LCM of 5, 10, 15 and 30 = 30

Question 3.
Solution:
We know that like fraction have same denominators
14,58,712,1324
LCM of 4, 8, 12, 24 = 24

Question 4.
Solution:

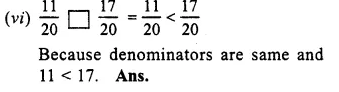
Question 5.
Solution:
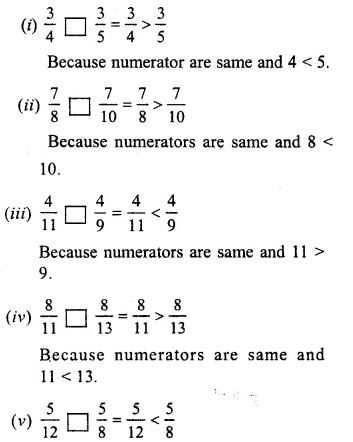
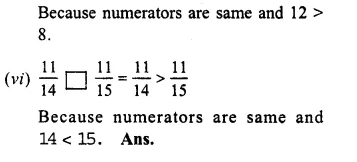
Compare the fractions given below :
Question 6.
Solution:
45and57
LCM of 5 and 7 = 35
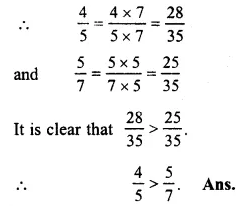
Question 7.
Solution:
38and56
LCM of 8 and 6 = 24
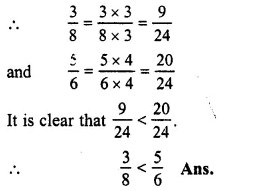
Question 8.
Solution:
711and67
LCM of 11 and 7 = 77
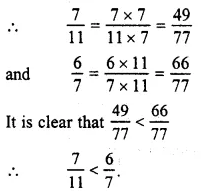
Question 9.
Solution:
56 and9 11
LCM of 6 and 11 = 66
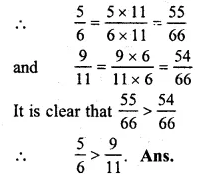
Question 10.
Solution:
23and49
LCM of 3 and 9 = 9

Question 11.
Solution:
613and34
LCM of 13 and 4 = 52
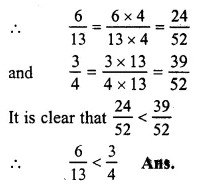
Question 12.
Solution:
34and56
LCM of 4 and 6 = 12
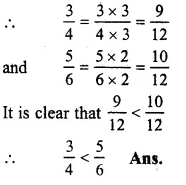
Question 13.
Solution:
58and712
LCM of 8 and 12 = 24

Question 14.
Solution:
49and56
LCM of 9 and 6 = 18
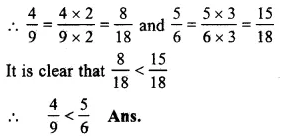
Question 15.
Solution:
45and710
LCM of 5 and 10 = 10
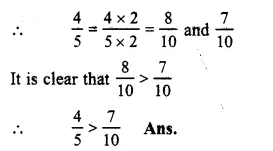
Question 16.
Solution:
78and910
LCM of 8 and 10 = 40

Question 17.
Solution:
1112and1315
LCM of 12 and 15 = 60

Question 18.
Solution:
12,34,56and78
LCM of 2, 4, 6 and 8 = 24

Question 19.
Solution:
23,56,79and1118
LCM of 3, 6, 9 and 18 = 18

Question 20.
Solution:
25,710,1115and1730
LCM of 5, 10, 15 and 30 = 30

Question 21.
Solution:
34,78,1116and2332
LCM of 4, 8, 16 and 32 = 32

Arrange the following fractions in the descending order :
Question 22.
Solution:
34,58,1112and1724
LCM of 4, 8, 12 and 24 = 24

Question 23.
Solution:
79,512,1118and1736
LCM of 9, 12, 18 and 36 = 36

Question 24.
Solution:
23,35,710and815
LCM of 3, 5, 10 and 15 = 30
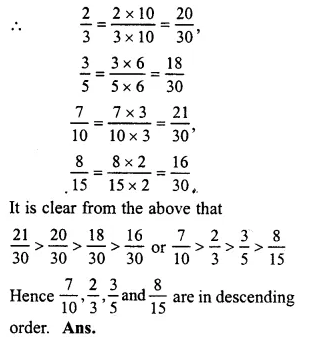
Question 25.
Solution:
57,914,1721and3142
LCM of 7, 14, 21 and 42 = 42

Question 26.
Solution:
∴ the numerators are equal
∴ The fraction having small denominator is greater than the fraction having large denominator
∴ In descending order, we can write
112,123,17,19,117,150
Question 27.
Solution:
Here, the numerators of all fractions are equal
∴ The fraction having small denominator is greater than the fraction having large denominator
Now in descending order is
34,35,37,311,313,317
Question 28.
Solution:
Lalita read 30 pages of a book containing 100 pages
She read 30100 = 310 part of the book and Sarita read 25 of the book
Now in 310 and 25, LCM of 10, 5 = 10
310 = 310
25 = 2×25×2 = 410
From above, Sarita read more
as 410 or 25>310
Question 29.
Solution:
Rafiq exercised for 23 hour and Rohit exercised for 34 hour
In 23 and 34, LCM of 3 and 4 = 12
23 = 2×43×4 = 812
34 = 3×34×3 = 912
912>812
=> 34>23
∴ Rohit exercised more time
Question 30.
Solution:
In VI A, 20 student passed out of 25 or 2025 or 45 students passed
But in VI B, 24 out of 30 passed 24 or 2430 or 45 students passed
Now 45 = 45
∴ Both sections gave same result
Ex 5E Solutions
Find the sum :
Question 1.
Solution:
58+18
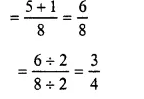
Question 2.
Solution:
49+89
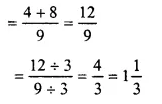
Question 3.
Solution:
135+245
85+145
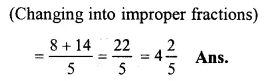
Question 4.
Solution:
25+56
= 4+1518 (LCM of 9 and 6 = 18)
= 1918
= 1118
Question 5.
Solution:
712+916

Question 6.
Solution:
415+1720
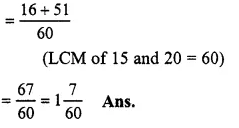
Question 7.
Solution:
234+556
= 114+356

Question 8.
Solution:
318+1512
= 258+1712

Question 9.
Solution:
2710+3815
= 2710+5315
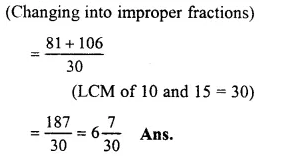
Question 10.
Solution:
323+156+2
113+116+21
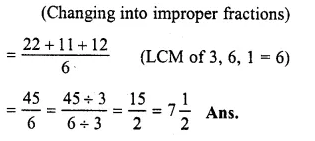
Question 11.
Solution:
3+1415+1320
=31+1915+2320
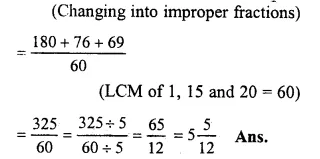
Question 12.
Solution:
313+414+616
103+174+376
(changing into improper fractions)
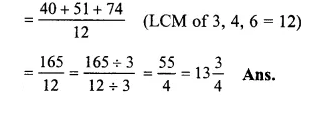
Question 13.
Solution:
23+316+429+2518
23+196+389+4118

Question 14.
Solution:
213+114+256+3712

Question 15.
Solution:
2+34+156+3716
21+34+138+5516

Question 16.
Solution:
Cost of a pencil = Rs. 325
Cost of an eraser = Rs.2710
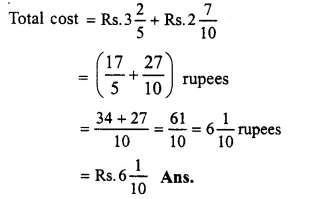
Question 17.
Solution:
Length of cloth for kurta = 412 metres
Length of cloth for pyjamas = 223 metres

Question 18.
Solution:
Distance travelled by Rickshaw = 434 km
Distance travelled on foot = 112 km

Question 19.
Solution:
Weight of empty cylinder = 1645 kg
Weight of gas filled in it = 1423 kg
Total. weight of cylinder with gas
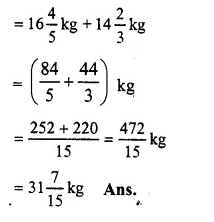
Ex 5F Solutions
Find the difference:
Question 1.
Solution:
58−18
= 5−18
= 48
= 4÷48÷4
= 12
Question 2.
Solution:
712−512

Question 3.
Solution:
437−247
= 317−187
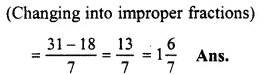
Question 4.
Solution:
56−49

Question 5.
Solution:
12−38

Question 6.
Solution:
58−712

Question 7.
Solution:
279−1815
= 259−2315
(changing into improper fractions)
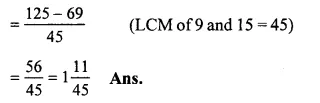
Question 8.
Solution:
358−2512
= 298−2912

Question 9.
Solution:
2310−1715
= 2310−2215

Question 10.
Solution:
623−334
= 203−154

Question 11.
Solution:
7−523
= 71−173
(changing into improper fractions)

Question 12.
Solution:
10−638
= 101−518
(changing into improper fractions)
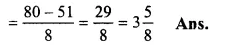
Simpilify
Question 13.
Solution:
56−49+23

Question 14.
Solution:
58+34−712
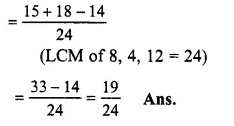
Question 15.
Solution:
2+1115−59
= 90+33−2545
(LCM of 15 and 9 = 45)
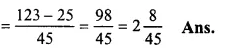
Question 16.
Solution:
534−4512+316
= 234−5312+196
(changing into improper fractions)
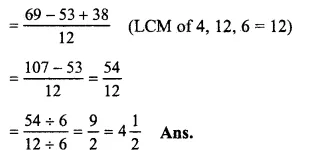
Question 17.
Solution:
2+5710−31415
= 21+5710−5915
(changing into improper fractions)

Question 18.
Solution:
8−312−214
= 81−72−94
(changing into improper fractions)
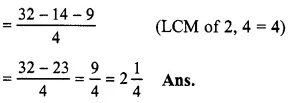
Question 19.
Solution:
856−338+2712
= 536−278+3112
(changing into improper fractions)
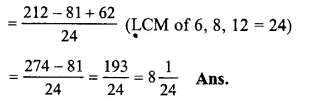
Question 20.
Solution:
616−515+313
= 376−265+103
(changing into improper fractions)

Question 21.
Solution:
3+115+23−715
= 31+65+23−715
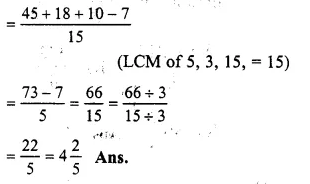
Question 22.
Solution:
By subtracting 923 from 19, we get the required number

Question 23.
Solution:
By subtracting 6715 from 815 we get the required number

Question 24.
Solution:
Sum of 359 and 313
= 329+103
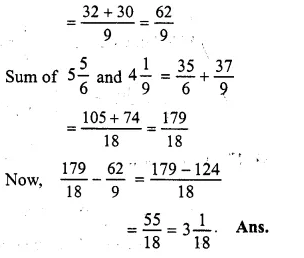
Question 25.
Solution:
34, 57

Question 26.
Solution:
Milk bought by Mrs. Soni = 712 litres
and milk consumed by here = 534 litres

Question 27.
Solution:
Total time of film show = 313 hours
Total spent on advertisement = 134 hours
Duration of the film

Question 28.
Solution:
On a day, rickshaw pullar earned

Question 29.
Solution:
Total length of wire =234-metres
Length of one piece = 58 metre
Length of the other piece
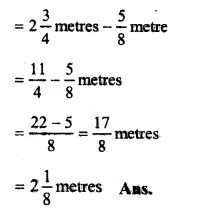
Ex 5G Solutions
Objective Questions :
Tick the correct answer in each of the following :
Question 1.
Solution:
(c) ∴ canceling the common factor 2, we get 35
Question 2.
Solution:
(c) ∴ multiplying numerator and denominator by 4, we get 812
Question 3.
Solution:
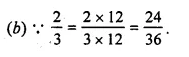
Question 4.
Solution:
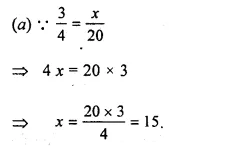
Question 5.
Solution:
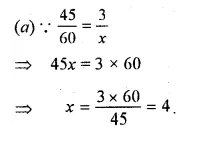
Question 6.
Solution:
(c) each of the fractions has the same denominator.
Question 7.
Solution:
(d) none of these has greater denominator than its numerator.
Question 8.
Solution:
(a) its denominator is greater than its numerator.
Question 9.
Solution:
(b) their numerators are same and 4 < 5 , 34>35
Question 10.
Solution:

Question 11.
Solution:
(b) In 45,27,49,411 numerator is same then the smallest denominator’s fraction is greater.
Question 12.
Solution:
(a) Denominators are same, then fraction of smallest numerator will be smallest.
Question 13.
Solution:

Question 14.
Solution:
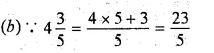
Question 15.
Solution:

Question 16.
Solution:
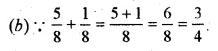
Question 17.
Solution:
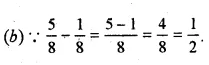
Question 18.
Solution:

Question 19.
Solution:

Question 20.
Solution:
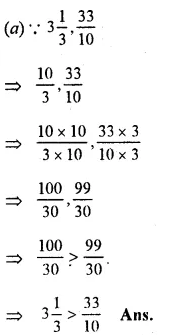
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5: Download PDF
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5–Fractions
Download PDF: RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5–Fractions PDF
Chapterwise RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths :
- Chapter 1–Number System
- Chapter 2–Factors and Multiples
- Chapter 3–Whole Numbers
- Chapter 4–Integers
- Chapter 5–Fractions
- Chapter 6–Simplification
- Chapter 7–Decimals
- Chapter 8–Algebraic Expressions
- Chapter 9–Linear Equations in One Variable
- Chapter 10–Ratio, Proportion and Unitary Method
- Chapter 11–Line Segment, Ray and Line
- Chapter 12–Parallel Lines
- Chapter 13–Angles and Their Measurement
- Chapter 14–Constructions (Using Ruler and a Pairs of Compasses)
- Chapter 15–Polygons
- Chapter 16–Triangles
- Chapter 17–Quadrilaterals
- Chapter 18–Circles
- Chapter 19–Three-Dimensional Shapes
- Chapter 20–Two-Dimensional Reflection Symmetry (Linear Symmetry)
- Chapter 21–Concept of Perimeter and Area
- Chapter 22–Data Handling
- Chapter 23–Pictograph
- Chapter 24–Bar Graph
About RS Aggarwal Class 6 Book
Investing in an R.S. Aggarwal book will never be of waste since you can use the book to prepare for various competitive exams as well. RS Aggarwal is one of the most prominent books with an endless number of problems. R.S. Aggarwal’s book very neatly explains every derivation, formula, and question in a very consolidated manner. It has tonnes of examples, practice questions, and solutions even for the NCERT questions.
He was born on January 2, 1946 in a village of Delhi. He graduated from Kirori Mal College, University of Delhi. After completing his M.Sc. in Mathematics in 1969, he joined N.A.S. College, Meerut, as a lecturer. In 1976, he was awarded a fellowship for 3 years and joined the University of Delhi for his Ph.D. Thereafter, he was promoted as a reader in N.A.S. College, Meerut. In 1999, he joined M.M.H. College, Ghaziabad, as a reader and took voluntary retirement in 2003. He has authored more than 75 titles ranging from Nursery to M. Sc. He has also written books for competitive examinations right from the clerical grade to the I.A.S. level.
FAQs
Why must I refer to the RS Aggarwal textbook?
RS Aggarwal is one of the most important reference books for high school grades and is recommended to every high school student. The book covers every single topic in detail. It goes in-depth and covers every single aspect of all the mathematics topics and covers both theory and problem-solving. The book is true of great help for every high school student. Solving a majority of the questions from the book can help a lot in understanding topics in detail and in a manner that is very simple to understand. Hence, as a high school student, you must definitely dwell your hands on RS Aggarwal!
Why should you refer to RS Aggarwal textbook solutions on Indcareer?
RS Aggarwal is a book that contains a few of the hardest questions of high school mathematics. Solving them and teaching students how to solve questions of such high difficulty is not the job of any neophyte. For solving such difficult questions and more importantly, teaching the problem-solving methodology to students, an expert teacher is mandatory!
Does IndCareer cover RS Aggarwal Textbook solutions for Class 6-12?
RS Aggarwal is available for grades 6 to 12 and hence our expert teachers have formulated detailed solutions for all the questions of each edition of the textbook. On our website, you’ll be able to find solutions to the RS Aggarwal textbook right from Class 6 to Class 12. You can head to the website and download these solutions for free. All the solutions are available in PDF format and are free to download!
