Class 11: Physics Chapter 8 solutions. Complete Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Notes.
Contents
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 8-Gravitation
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
Page No: 201
Excercises
8.1. Answer the following:
(a)You can shield a charge from electrical forces by putting it inside a hollow conductor. Can you shield a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter by putting it inside a hollow sphere or by some other means?
(b) An astronaut inside a small space ship orbiting around the earth cannot detect gravity. If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size, can he hope to detect gravity?
(c) If you compare the gravitational force on the earth due to the sun to that due to the moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the moon’s pull. (You can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of sun. Why?
Answer
(a) We cannot shiwld a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter, because the gravitational force on a body due to nearby matter is independent of the presence of other matter, whereas it is not so in case of electric forces. It means the gravitational screens are not possible.
(b) Yes, if the size of the space station is large enough, then the astronaut will detect the change in Earth’s gravity (g).
(c) Tidal effect depends inversely upon the cube of the distance while, gravitational force depends inversely on the square of the distance. Since the distance between the Moon and the Earth is smaller than the distance between the Sun and the Earth, the tidal effect of the Moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of the Sun’s pull.
8.2. Choose the correct alternative:
(a) Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing altitude.
(b)Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing depth. (assume the earth to be a sphere of uniform density).
(c)Acceleration due to gravity is independent of mass of the earth/mass of the body.
(d)The formula –G Mm(1/r2– 1/r1) is more/less accurate than the formula mg(r2– r1) for the difference of potential energy between two points r2and r1distance away from the centre of the earth.
Answer
(a) decreases
(b) decreases
(c) mass of the body
(d) more.
8.3. Suppose there existed a planet that went around the sun twice as fast as the earth.What would be its orbital size as compared to that of the earth?
Answer
Time taken by the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun,
Te = 1 year
Orbital radius of the Earth in its orbit, Re = 1 AU
Time taken by the planet to complete one revolution around the Sun, TP = ½Te = ½ year
Orbital radius of the planet = Rp
From Kepler’s third law of planetary motion, we can write:
(Rp / Re)3 = (Tp / Te)2
(Rp / Re) = (Tp / Te)2/3
= (½ / 1)2/3 = 0.52/3 = 0.63
Hence, the orbital radius of the planet will be 0.63 times smaller than that of the Earth.
8.4. Io, one of the satellites of Jupiter, has an orbital period of 1.769 days and the radius of the orbit is 4.22 × 108 m. Show that the mass of Jupiter is about one-thousandth that of the sun.
Answer
Orbital period of I0 , TI0 = 1.769 days = 1.769 × 24 × 60 × 60 s
Orbital radius of I0 , RI0 = 4.22 × 108 m
Satellite I0 is revolving around the Jupiter
Mass of the latter is given by the relation:
MJ = 4π2RI03 / GTI02 …..(i)
Where,
MJ = Mass of Jupiter
G = Universal gravitational constant
Orbital period of the earth,
Te = 365.25 days = 365.25 × 24 × 60 × 60 s
Orbital radius of the Earth,
Re = 1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m
Mass of sun is given as:
Ms = 4π2Re3 / GTe2 ……(ii)
∴ Ms / MJ = (4π2Re3 / GTe2) × (GTI02 / 4π2RI03) = (Re3 × TI02) / (RI03 × Te2)
Substituting the values, we get:
= (1.769 × 24 × 60 × 60 / 365.25 × 24 × 60 × 60)2 × (1.496 × 1011 / 4.22 × 108)3
= 1045.04
∴ Ms / MJ ~ 1000
Ms ~ 1000 × MJ
Hence, it can be inferred that the mass of Jupiter is about one-thousandth that of the Sun.
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
8.5. Let us assume that our galaxy consists of 2.5 × 1011 stars each of one solar mass. How long will a star at a distance of 50,000 ly from the galactic centre take to complete one revolution? Take the diameter of the Milky Way to be 105 ly.
Answer
Mass of our galaxy Milky Way, M = 2.5 × 1011 solar mass
Solar mass = Mass of Sun = 2.0 × 1036 kg
Mass of our galaxy, M = 2.5 × 1011 × 2 × 1036 = 5 × 1041 kg
Diameter of Milky Way, d = 105 ly
Radius of Milky Way, r = 5 × 104 ly
1 ly = 9.46 × 1015 m
∴r = 5 × 104 × 9.46 × 1015
= 4.73 ×1020 m
Since a star revolves around the galactic centre of the Milky Way, its time period is given by the relation:
T = ( 4π2r3 / GM)1/2
= [ (4 × 3.142 × 4.733 × 1060) / (6.67 × 10-11 × 5 × 1041) ]1/2
= (39.48 × 105.82 × 1030 / 33.35 )1/2
= 1.12 × 1016 s
1 year = 365 × 324 × 60 × 60 s
1s = 1 / (365 × 324 × 60 × 60) years
∴ 1.12 × 1016 s = 1.12 × 1016 / (365 × 24 × 60 × 60) = 3.55 × 108 years.
8.6. Choose the correct alternative:
(a) If the zero of potential energy is at infinity, the total energy of an orbiting satellite is negative of its kinetic/potential energy.
(b) The energy required to launch an orbiting satellite out of earth’s gravitational influence is more/less than the energy required to project a stationary object at the same height (as the satellite) out of earth’s influence.
Answer
(a) Kinetic energy
(b) Less
8.7. Does the escape speed of a body from the earth depend on
(a) the mass of the body,
(b) the location from where it is projected,
(c) the direction of projection,
(d) the height of the location from where the body is launched?
Answer
The escape velocity is indpendent of the mass of the body and the direction of projection. It depends upon the gravitational potential at the point from where the body is launched. Since, this potential depends slightly on the latitude and height of the point, therefore, the escape velocity depends slightly on these factors.
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
8.8. A comet orbits the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit. Does the comet have a constant (a) linear speed, (b) angular speed, (c) angular momentum, (d) kinetic energy, (e) potential energy, (f) total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the Sun.
Answer
A comet while going on elliptical orbit around the Sun has constant angular momentum and totaal energy at all locations but other quantities vary with locations.
8.9. Which of the following symptoms is likely to afflict an astronaut in space (a) swollen feet, (b) swollen face, (c) headache, (d) orientational problem?
Answer
(a) Legs hold the entire mass of a body in standing position due to gravitational pull. In space, an astronaut feels weightlessness because of the absence of gravity. Therefore, swollen feet of an astronaut do not affect him/her in space.
(b) A swollen face is caused generally because of apparent weightlessness in space. Sense organs such as eyes, ears nose, and mouth constitute a person’s face. This symptom can affect an astronaut in space.
(c) Headaches are caused because of mental strain. It can affect the working of an astronaut in space.
(d) Space has different orientations. Therefore, orientational problem can affect an astronaut in space.
8.10. Choose the correct answer from among the given ones:The gravitational intensity at the centre of a hemispherical shell of uniform mass density has the direction indicated by the arrow (see Fig 8.12) (i) a, (ii) b, (iii) c, (iv) O.
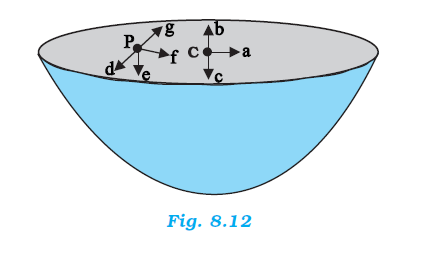
Answer
Gravitational potential (V) is constant at all points in a spherical shell. Hence, the gravitational potential gradient (dV/dR) is zero everywhere inside the spherical shell. The gravitational potential gradient is equal to the negative of gravitational intensity. Hence, intensity is also zero at all points inside the spherical shell. This indicates that gravitational forces acting at a point in a spherical shell are symmetric.
If the upper half of a spherical shell is cut out (as shown in the given figure), then the net gravitational force acting on a particle located at centre O will be in the downward direction.
Since gravitational intensity at a point is defined as the gravitational force per unit mass at that point, it will also act in the downward direction. Thus, the gravitational intensity at centre O of the given hemispherical shell has the direction as indicated by arrow c.
8.11. Choose the correct answer from among the given ones:
For the problem 8.10, the direction of the gravitational intensity at an arbitrary point P is indicated by the arrow (i) d, (ii) e, (iii) f, (iv) g.
Answer
Gravitational potential (V) is constant at all points in a spherical shell. Hence, the gravitational potential gradient (dV/dR) is zero everywhere inside the spherical shell. The gravitational potential gradient is equal to the negative of gravitational intensity. Hence, intensity is also zero at all points inside the spherical shell. This indicates that gravitational forces acting at a point in a spherical shell are symmetric.
If the upper half of a spherical shell is cut out (as shown in the given figure), then the net gravitational force acting on a particle at an arbitrary point P will be in the downward direction.
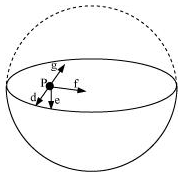
Since gravitational intensity at a point is defined as the gravitational force per unit mass at that point, it will also act in the downward direction. Thus, the gravitational intensity at an arbitrary point P of the hemispherical shell has the direction as indicated by arrow e.
Hence, the correct answer is (ii).
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
8.12. A rocket is fired from the earth towards the sun. At what distance from the earth’s centre is the gravitational force on the rocket zero? Mass of the sun = 2 ×1030 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg. Neglect the effect of other planets etc. (orbital radius = 1.5 × 1011 m).
Answer
Mass of the Sun, Ms = 2 × 1030 kg
Mass of the Earth, Me = 6 × 10 24 kg
Orbital radius, r = 1.5 × 1011 m
Mass of the rocket = m
Let x be the distance from the centre of the Earth where the gravitational force acting on satellite P becomes zero.
From Newton’s law of gravitation, we can equate gravitational forces acting on satellite P under the influence of the Sun and the Earth as:
GmMs / (r – x)2 = GmMe / x2
[ (r – x) / x ]2 = Ms / Me
(r – x) / x = [ 2 × 1030 / 60 × 1024]1/2 = 577.35
1.5 × 1011 – x = 577.35x
578.35x = 1.5 × 1011
x = 1.5 × 1011 / 578.35 = 2.59 × 108 m.
8.13.How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 1.5 × 108 km.
Answer
Orbital radius of the Earth around the Sun, r = 1.5 × 1011 m
Time taken by the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun,
T = 1 year = 365.25 days
= 365.25 × 24 × 60 × 60 s
Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67 × 10–11 Nm2 kg–2
Thus, mass of the Sun can be calculated using the relation,
M = 4π2r3 / GT2
= 4 × 3.142 × (1.5 × 1011)3 / [ 6.67 × 10-11 × (365.25 × 24 × 60 × 60)2]
= 2 × 1030 kg
Hence, the mass of the Sun is 2 × 1030 kg.
8.14. A Saturn year is 29.5 times the earth year. How far is the Saturn from the sun if the earth is 1.50 ×108 km away from the sun?
Answer
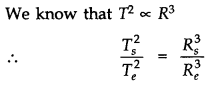

NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
Question 8. 15. A body weighs 63 N on the surface of the Earth. What is the gravitational force on it due to the Earth at a height equal to half the radius of the Earth?
Answer
Let gh be the acceleration due to gravity at a height equal to half the radius of the Earth (h = R/2) and g its value on Earth’s surface. Let the body have mass m.

Question 8. 16. Assuming the earth to be a sphere of uniform mass density, how much would a body weigh half way down to the centre of the earth if it weighed 250 N on the surface?
Answer
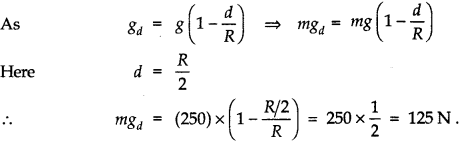
Question 8. 17. A rocket is fired vertically with a speed of 5 km s-1 from the earth’s surface. How far from the earth does the rocket go before returning to the earth? Mass of the earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg; mean radius of the earth = 6.4 x 106 m; G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2.
Answer
Initial kinetic energy of rocket = 1/2 mv2 = 1/2 x m x (5000)2 = 1.25 x 107 mJ
At distance r from centre of earth, kinetic energy becomes zero
.•. Change in kinetic energy = 1.25 x 107 – 0 = 1.25 x 107 m J
This energy changes into potential energy.
Initial potential energy at the surface of earth = GMem/’r

Question 8. 18. The escape speed of a projectile on the Earth’s surface is 11.2 km s-1. A body is projected out with thrice this speed. What is the speed of the body far away from the Earth? Ignore the presence of the Sun and other planets.
Answer

NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
Question 8. 19. A satellite orbits the earth at a height of 400 km above the surface. How much energy must be expended to rocket the satellite out of the earth’s gravitational influence? Mass of the satellite = 200 kg; mass of the earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg; radius of the earth = 6.4 x 106 m; G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2.
Answer
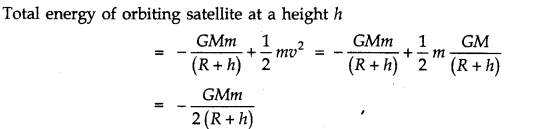

Question 8. 20. Two stars each of one solar mass (=2 x 1030 kg) are approaching each other for a head on collision.When they are at a distance 109 km, their speeds are negligible. What is the speed with which they collide? The radius of each star is 104 km. Assume the stars to remain undistorted until they collide. (Use the known value of G).
Answer
Here, mass of each star, M = 2 x 1030 kg
Initial potential between two stars, r = 109 km = 1012 m.
Initial potential energy of the system = -GMm/r
Total K.E. of the stars = 1/2Mv2 + 1/2Mv2
where v is the speed of stars with which they collide. When the stars are about to collide, the distance between their centres, r’ = 2 R.
:. Final potential energy of two stars = -GMm/2R
Since gain in K.E. is at the cost of loss in P.E

NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 8, class 11 Physics chapter 8 solutions
Question 8. 21. Two heavy spheres each of mass 100 kg and radius 0.10 mare placed 1.0 m apart on ahorizontal table. What is the gravitational field and potential at the mid point of the line joining the centres of the spheres ? Is an object placed at that point in equilibrium ? If so, is the equilibrium stable or unstable?
Answer
Here G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2 kg-2; M = 100 kg; R = 0.1 m, distance between the two spheres, d = 1.0 m
Suppose that the distance of either sphere from the mid-point of the line joining their centre is r. Then r=d/2=0.5 m. The gravitational field at the mid-point due to two spheres will be equal and opposite.

Question 8. 22. As you have learnt in the text, a geostationary satellite orbits the Earth at a height of nearly 36,000 km from the surface of the Earth. What is the potential due to Earth’s gravity at the site of this satellite? (Take the potential energy at infinity to be zero). Mass of the Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg, radius = 6400 km.
Answer
Distance of satellite from the centre of earth = R = r + x
= 6400 + 36000 = 42400 km = 4.24 x 107 m
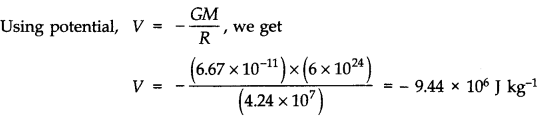
Question 8. 23. A star 2.5 times the mass of the sun and collapsed to a size of 12 km rotates with a speed of 1.2 rev. per second. (Extremely compact stars of this kind are known as neutron stars. Certain stellar objects called pulsars belong to this category). Will an object placed on its equator remain stuck to its surface due to gravity? (mass of the sun = 2 x 1030 kg).
Answer
Acceleration due to gravity of the star,g= GM/R2 …………(i)
Here M is the mass and R is the radius of the star.
The outward centrifugal force acting on a body of mass m at the equator of the star =mv2/R =mR w2——-(ii)
From equation (i), the acceleration due to the gravity of the star
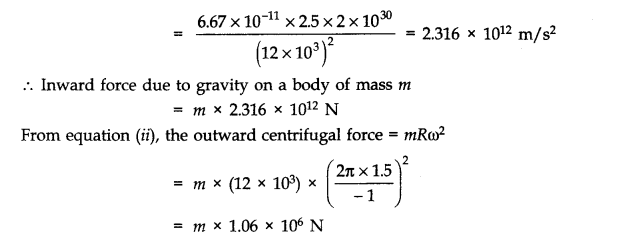
Since the inward force due to gravity on a body at the equator of the star is about 2.2 million times more than the outward centrifugal force, the body will remain stuck to the surface of the star.
Question 8. 24. A spaceship is stationed on Mars. How much energy must be expended on the spaceship to rocket it out of the solar system? Mass of the spaceship = 1000 kg, Mass of the Sun = 2 x 1030 kg. Mass of the Mars = 6.4 x 1023 kg, Radius of Mars = 3395 km. Radius of the orbit of Mars = 2.28 x 1011 m, G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2.
Answer
Let R be the radius of orbit of Mars and R’ be the radius of the Mars. M be the mass of the Sun and M’ be the mass of Mars. If m is the mass of the space-ship, then Potential energy of space-ship due to gravitational attraction of the Sun = – GM m/R Potential energy of space-ship due to gravitational attraction of Mars = – G M’ m/R’ Since the K.E. of space ship is zero, therefore,
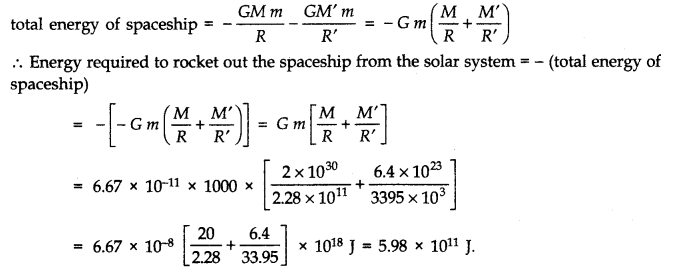
Question 8. 25. A rocket is fired ‘vertically’ from the surface of Mars with a speed of 2 km s-1. If 20% of its initial energy is lost due to Martian atmospheric resistance, how far will the rocket go from the surface of mars before returning to it? Mass of Mars = 6.4 x 1023 kg; radius of Mars = 3395 km; G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2
Answer

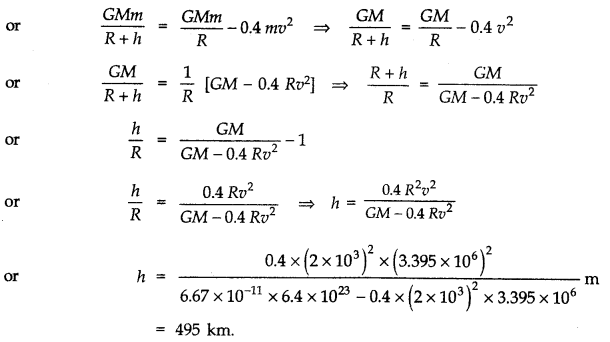
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 8: Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 8-Gravitation
Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 8-Gravitation PDF
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics:
- Chapter 1-Physical World
- Chapter 2-Units and Measurements
- Chapter 3-Motion In A Straight Line
- Chapter 4-Motion In A Plane
- Chapter 5-Laws Of Motion
- Chapter 6-Work, Energy And Power
- Chapter 7-System Of Particles And Rotational Motion
- Chapter 8-Gravitation
- Chapter 9-Mechanical properties of Solids
- Chapter 10-Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Chapter 11-Thermal Properties of Matter
- Chapter 12-Thermodynamics
- Chapter 13-Kinetic Theory
- Chapter 14-Oscillations
- Chapter 15-Waves
About NCERT
The National Council of Educational Research and Training is an autonomous organization of the Government of India which was established in 1961 as a literary, scientific, and charitable Society under the Societies Registration Act. Its headquarters are located at Sri Aurbindo Marg in New Delhi. Visit the Official NCERT website to learn more.
