Class 11: Physics Chapter 2 solutions. Complete Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Notes.
Contents
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 2-Units and Measurements
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 2, class 11 Physics chapter 2 solutions
Page No: 35
Exercises
2.1. Fill in the blanks
(a) The volume of a cube of side 1 cm is equal to…..m3
(b) The surface area of a solid cylinder of radius 2.0 cm and height 10.0 cm is equal to … (mm)2
(c) A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h–1covers….m in 1 s
(d) The relative density of lead is 11.3. Its density is ….g cm–3or . …kg m–3.
Answer
(a) Length of edge = 1cm = 1/100 m
Volume of the cube = side3
Putting the value of side, we get
Volume of the cube = (1/100 m)3
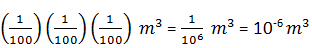
The volume of a cube of side 1 cm is equal to 10
-6 m3
(b) Given,
Radius, r = 2.0 cm = 20 mm (convert cm to mm)
Height, h = 10.0 cm =100 mm
The formula of total surface area of a cylinder S = 2πr (r + h)
Putting the values in this formula, we get
Surface area of a cylinder S = 2πr (r + h = 2 x 3.14 x 20 (20+100)
= 15072 = 1.5 × 104 mm2
The surface area of a solid cylinder of radius 2.0 cm and height 10.0 cm is equal to 1.5 × 10
4 mm2
(c) Using the conversion,
Given,
Time, t = 1 sec
speed = 18 km h-1 = 18 km / hour
1 km = 1000 m and 1hour = 3600 sec
Speed = 18 × 1000 /3600 sec = 5 m /sec
Use formula
Speed = distance / time
Cross multiply it, we get
Distance = Speed × Time = 5 × 1 = 5 m
A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h–1covers 5
m in 1 s.
(d) Density of lead = Relative density of lead × Density of water
Density of water = 1 g/cm3
Putting the values, we get
Density of lead = 11.3 × 1 g/ cm3
= 11.3 g cm-3
1 cm = (1/100 m) =10–2 m3
1 g = 1/1000 kg = 10-3 kg
Density of lead = 11.3 g cm-3 = 11.3
Putting the value of 1 cm and 1 gram
11.3 g/cm3 = 11.3 × 10-3 kg (10-2m)-3 = 11.3 ×10–3 × 106 kg m-3 =1.13 × 103 kg m–3
The relative density of lead is 11.3. Its density is 11.3
g cm-3 g cm–3 or 1.13 × 10
3 kg m–3.
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 2, class 11 Physics chapter 2 solutions
2.2. Fill in the blanks by suitable conversion of units:
(a) 1 kg m2s–2= ….g cm2 s–2
(b) 1 m =….. ly
(c) 3.0 m s–2=…. km h–2
(d) G= 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 (kg)–2=…. (cm)3s–2 g–1.
Answer
(a) 1 kg = 103 g
1 m2 = 104 cm2
1 kg m2 s–2 = 1 kg × 1 m2 × 1 s–2
=103 g × 104 cm2 × 1 s–2 = 107 g cm2 s–2
1 kg m2s–2= 10
7 g cm2 s–2
(b) Distance = Speed × Time
Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s
Time = 1 year = 365 days = 365 × 24 hours = 365 × 24 × 60 × 60 sec
Putting these values in above formula we get
1 light year distance = (3 × 108 m/s) × (365 × 24 × 60 × 60 s) = 9.46 × 1015 m
9.46 × 1015 m = 1 ly
So that 1 m = 1/ 9.46 × 1015 ly = 1.06 × 10
-16 ly
(c) 1 hour = 3600 sec so that 1 sec = 1/3600 hour
1 km = 1000 m so that 1 m = 1/1000 km
3.0 m s–2 = 3.0 (1/1000 km)( 1/3600 hour)-2 = 3.0 × 10–3 km × ((1/3600)-2 h–2)
= 3.0 × 10–3 km × (3600)2 h–2 = 3.88 × 104 km h–2
3.0 m s–2= 3.88 × 10
4 km h–2
(d) Given,
G= 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 (kg)–2
We know that
1 N = 1 kg m s–2
1 kg = 103 g
1 m = 100 cm = 102 cm
Putting above values, we get
6.67 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2 = 6.67 × 10–11 × (1 kg m s–2) (1 m2) (1Kg–2)
Solve and cancel out the units we get
⇒ 6.67 × 10–11 × (1 kg–1 × 1 m3 × 1 s–2)
Putting above values to convert Kg to g and m to cm
⇒ 6.67 × 10–11 × (103 g)-1 × (102 cm)3 × (1 s–2)
⇒ 6.67 × 10–11 × 10-3 g-1 × 106 cm3 × (1 s–2)
⇒ 6.67 × 10–8 cm3 s–2 g–1
G= 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 (kg)–2= 6.67 × 10
–8 (cm)3s–2 g–1.
2.3. A calorie is a unit of heat or energy and it equals about 4.2 J where 1J = 1 kg m2s–2. Suppose we employ a system of units in which the unit of mass equals α kg, the unit of length equals β m, the unit of time is γ s. Show that a calorie has a magnitude 4.2 α–1 β–2 γ2 in terms of the new units.
Answer
Given that,
1 Calorie=4.2 J = 4.2 Kg m2 s-2 …… (i)
As new unit of mass = α Kg
∴ 1 Kg = 1/α new unit of mass
Similarly, 1 m = β-1 new unit of length
1 s = γ-1 new unit of time
Putting these values in (i), we get
1 calorie = 4.2 (α-1 new unit of mass) (β-1 new unit of length)2 (γ-1 new unit of time)-2
= 4.2 α-1 β-2 γ2 new unit of energy (Proved)
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 2, class 11 Physics chapter 2 solutions
2.4. Explain this statement clearly:
“To call a dimensional quantity ‘large’ or ‘small’ is meaningless without specifying a standard for comparison”. In view of this, reframe the following statements wherever necessary:
(a) atoms are very small objects
(b) a jet plane moves with great speed
(c) the mass of Jupiter is very large
(d) the air inside this room contains a large number of molecules
(e) a proton is much more massive than an electron
(f) the speed of sound is much smaller than the speed of light.
Answer
The given statement is true because a dimensionless quantity may be large or small in comparision to some standard reference. For example, the coefficient of friction is dimensionless. The coefficient of sliding friction is greater than the coefficient of rolling friction, but less than static friction.
(a) An atom is a very small object in comparison to a soccer ball.
(b) A jet plane moves with a speed greater than that of a bicycle.
(c) Mass of Jupiter is very large as compared to the mass of a cricket ball.
(d) The air inside this room contains a large number of molecules as compared to that present in a geometry box.
(e) A proton is more massive than an electron.
(f) Speed of sound is less than the speed of light.
2.5. A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in vacuum is unity. What is the distance between the Sun and the Earth in terms of the new unit if light takes 8 min and 20 s to cover this distance?
Answer
Distance between the Sun and the Earth = Speed of light x Time taken by light to cover the distance
Given that in the new unit, speed of light = 1 unit
Time taken, t = 8 min 20 s = 500 s
∴Distance between the Sun and the Earth = 1 x 500 = 500 units
NCERT 11th Physics Chapter 2, class 11 Physics chapter 2 solutions
2.6. Which of the following is the most precise device for measuring length:
(a) a vernier callipers with 20 divisions on the sliding scale
(b) a screw gauge of pitch 1 mm and 100 divisions on the circular scale
(c) an optical instrument that can measure length to within a wavelength of light?
Answer
(a) Least count of this vernier callipers = 1SD – 1 VD = 1 SD – 19/20 SD = 1/20 SD
= 1.20 mm = 1/200 cm = 0.005 cm
(b) Least count of screw gauge = Pitch/Number of divisions = 1/1000 = 0.001 cm.
(c) Wavelength of light, λ ≈ 10-5 cm = 0.00001 cm
Hence, it can be inferred that an optical instrument is the most suitable device to measure length.
2.7. A student measures the thickness of a human hair by looking at it through a microscope of magnification 100. He makes 20 observations and finds that the average width of the hair in the field of view of the microscope is 3.5 mm. What is the estimate on the thickness of hair?
Magnification of the microscope = 100
Average width of the hair in the field of view of the microscope = 3.5 mm
∴Actual thickness of the hair is 3.5/100 = 0.035 mm.
2.8. Answer the following:
(a) You are given a thread and a metre scale. How will you estimate the diameter of the thread?
Answer
Wrap the thread on a uniform smooth rod in such a way that the coils thus formed are very close to each other. Measure the length of the thread using a metre scale. The diameter of the thread is given by the relation,
Diameter = Length of thread/Number of turns
(b) A screw gauge has a pitch of 1.0 mm and 200 divisions on the circular scale. Do you think it is possible to increase the accuracy of the screw gauge arbitrarily by increasing the number of divisions on the circular scale?
Answer
It is not possible to increase the accuracy of a screw gauge by increasing the number of divisions of the circular scale. Increasing the number divisions of the circular scale will increase its accuracy to a certain extent only.
(c) The mean diameter of a thin brass rod is to be measured by vernier callipers. Why is a set of 100 measurements of the diameter expected to yield a more reliable estimate than a set of 5 measurements only?
Answer
A set of 100 measurements is more reliable than a set of 5 measurements because random errors involved in the former are very less as compared to the latter.
2.9. The photograph of a house occupies an area of 1.75 cm2on a 35 mm slide. The slide is projected on to a screen, and the area of the house on the screen is 1.55 m2. What is the linear magnification of the projector-screen arrangement?
Answer
Area of the house on the slide = 1.75 cm2
Area of the image of the house formed on the screen = 1.55 m2 = 1.55 × 104 cm2
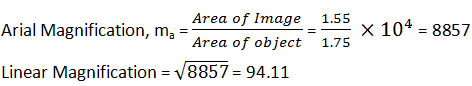
2.10. State the number of significant figures in the following:
(a) 0.007 m2
► 1
(b) 2.64 x 1024 kg
► 3
(c) 0.2370 g cm-3
► 4
(d) 6.320 J
► 4
(e) 6.032 N m-2
► 4
(f) 0.0006032 m2
► 4
Page No: 36
2.11. The length, breadth and thickness of a rectangular sheet of metal are 4.234 m, 1.005 m, and 2.01 cm respectively. Give the area and volume of the sheet to correct significant figures.
Answer
Given that,
length, l = 4.234 m
breadth,b = 1.005 m
thickness, t = 2.01 cm = 2.01 × 10-2 m
Area of the sheet = 2 (l × 0 + b × t + t × l) = 2 (4.234 × 1.005 + 1.005 × 0.0201 + 0.0201 × 4.234)
= 2 (4.3604739) = 8.7209478 m2
As area can contain a maximum of three significant digits, therefore, rounding off, we get
Area = 8.72 m2
Also, volume = l × b × t
V = 4.234 × 1.005 × 0.0201 = 0.0855289 = 0.0855 m3 (Significant Figures = 3)
2.12. The mass of a box measured by a grocer’s balance is 2.300 kg. Two gold pieces of masses 20.15 g and 20.17 g are added to the box. What is (a) the total mass of the box, (b) the difference in the masses of the pieces to correct significant figures?
Answer
Mass of grocer’s box = 2.300 kg
Mass of gold piece I = 20.15g = 0.02015 kg
Mass of gold piece II = 20.17 g = 0.02017 kg
(a) Total mass of the box = 2.3 + 0.02015 + 0.02017 = 2.34032 kg
In addition, the final result should retain as many decimal places as there are in the number with the least decimal places. Hence, the total mass of the box is 2.3 kg.
(b) Difference in masses = 20.17 – 20.15 = 0.02 g
In subtraction, the final result should retain as many decimal places as there are in the number with the least decimal places.
2.13. A physical quantity P is related to four observables a, b, c and d as follows:
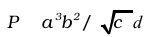
The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c and d are 1%, 3%, 4% and 2%, respectively. What is the percentage error in the quantity P? If the value of P calculated using the above relation turns out to be 3.763, to what value should you round off the result?
Answer
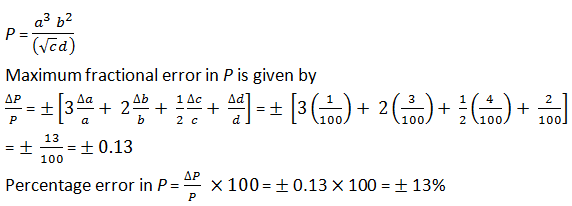
Percentage error in P = 13 %
Value of P is given as 3.763.
By rounding off the given value to the first decimal place, we get P = 3.8.
2.14. A book with many printing errors contains four different formulas for the displacement y of a particle undergoing a certain periodic motion:

(a = maximum displacement of the particle, v = speed of the particle. T = time-period of motion). Rule out the wrong formulas on dimensional grounds.
Answer
The displacement y has the dimension of length, therefore, the formula for it should also have the dimension of length. Trigonometric functions are dimensionless and their arguments are also dimensionless. Based on these considerations now check each formula dimensionally.
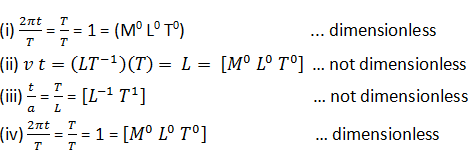
The formulas in (ii) and (iii) are dimensionally wrong.
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 2: Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 2-Units and Measurements
Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for 11th Class Physics: Chapter 2-Units and Measurements PDF
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics:
- Chapter 1-Physical World
- Chapter 2-Units and Measurements
- Chapter 3-Motion In A Straight Line
- Chapter 4-Motion In A Plane
- Chapter 5-Laws Of Motion
- Chapter 6-Work, Energy And Power
- Chapter 7-System Of Particles And Rotational Motion
- Chapter 8-Gravitation
- Chapter 9-Mechanical properties of Solids
- Chapter 10-Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Chapter 11-Thermal Properties of Matter
- Chapter 12-Thermodynamics
- Chapter 13-Kinetic Theory
- Chapter 14-Oscillations
- Chapter 15-Waves
About NCERT
The National Council of Educational Research and Training is an autonomous organization of the Government of India which was established in 1961 as a literary, scientific, and charitable Society under the Societies Registration Act. Its headquarters are located at Sri Aurbindo Marg in New Delhi. Visit the Official NCERT website to learn more.
