Class 7: Maths Chapter 13 solutions. Complete Class 7 Maths Chapter 13 Notes.
Contents
ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
ML Aggarwal 7th Maths Chapter 13, Class 7 Maths Chapter 13 solutions
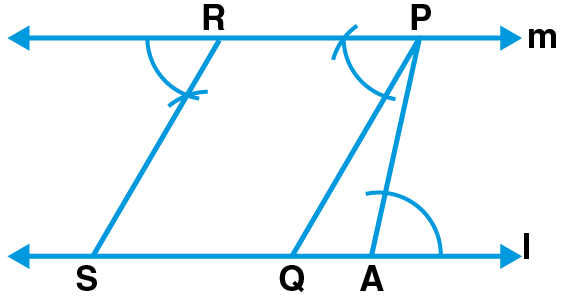
1. Let l be a line and P be a point not on l. Through P, draw a line m parallel to l. Now join P to any point Q on l. Choose any other point R on m. Through R, draw a line parallel to PQ. If this line meets l at S, then what shape do the two sets of parallel lines inclose?
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line l and P be a point not on the line l
(ii) Take a point A on line l and join PA
(iii) Draw a line m which is parallel to line l on point P
(iv) Take a point Q on line l and join PQ
(v) From a point R on line m, draw a line parallel to PQ which meets l at point S
Here,
We can observe that PQRS is a parallelogram
2. Construct a triangle ABC, given that
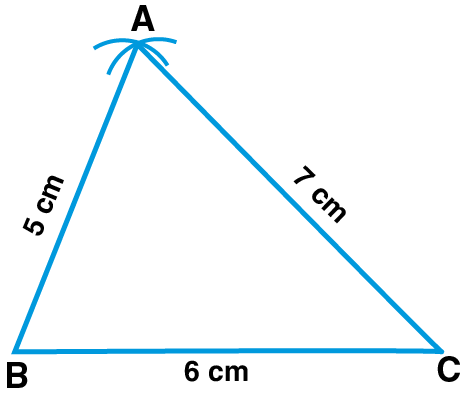
(i) AB = 5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 7 cm
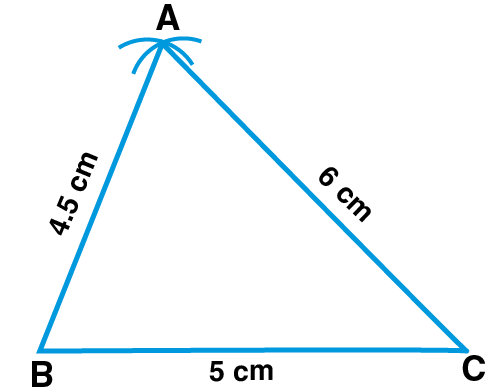
(ii) AB = 4.5 cm, BC = 5 cm and AC = 6 cm
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment BC such that BC = 6 cm
2. Taking B as centre and radius 5 cm and taking C as centre and radius 7 cm, draw arcs which intersect each other at point A
3. Now, join AB and AC
Therefore,
△ABC is the required triangle
(ii) Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment BC such that BC = 5 cm
2. Taking B as centre and radius 4.5 cm and taking C as centre and radius 6 cm, draw arcs which intersect each other at point A
3. Now, join AB and AC
Therefore,
△ABC is the required triangle
3. Construct a triangle PQR given that PQ = 5.4 cm, QR = PR = 4.7 cm. Name the triangle.
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ of length 5.4 cm
2. Taking P and Q as centres and radius 4.7 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at point R
3. Join PR and QR
Here, the two sides are equal of length 4.7 cm
Hence, the required △RPQ is an isosceles triangle

4. Construct a triangle LMN such that the length of each side is 5.4 cm. Name the triangle.
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment MN such that MN = 5.4 cm
2. Taking M and N as centres and radius 5.4 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at point L
Here, we can observe that all the sides of triangle = 5.4 cm
Therefore,
The required △LMN is an equilateral triangle

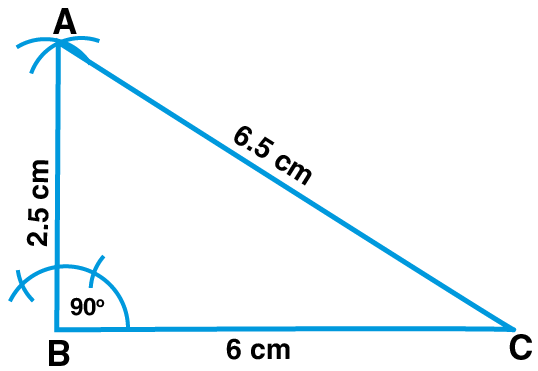
5. Construct a triangle ABC such that AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm. Measure ∠ABC and name the triangle
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment such that BC = 6 cm
2. Taking B as centre and radius 2.5 cm and taking C as centre and radius 6.5 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at point A
3. Join AB and AC
Now, the △ABC is the required triangle
On measuring, we get, ∠ABC = 900
Hence, △ABC is a right angled triangle
6. Construct a triangle PQR, given that PQ = 3 cm, QR = 5.5 cm and ∠PQR = 600
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment QR of length 5.5 cm
2. Taking Q as centre, draw a ray QX making an angel of 600
3. Now, cut off PQ = 3 cm
4. Join PR
Therefore,
△PQR is the required triangle

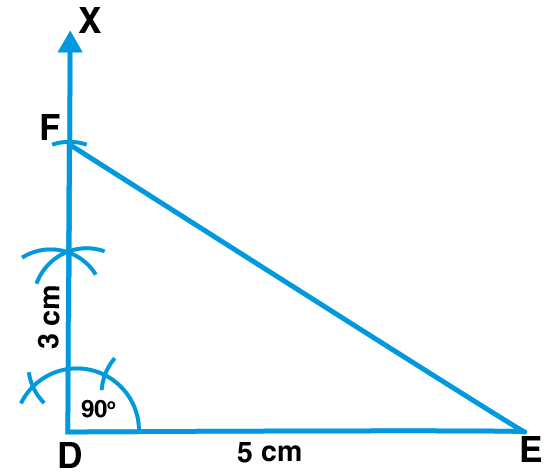
7. Construct △DEF such that DE = 5 cm, DF = 3 cm and ∠EDF = 900
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment DE of length 5 cm
2. Taking D as centre, draw a ray DX making an angle of 900
3. Now, cut off DF = 3 cm
4. Join FE
△FDE is the required triangle
Download PDF
ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
Download PDF: ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry PDF
Chapterwise ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 7 Maths :
- Chapter 1- Integers
- Chapter 2- Fractions and Decimals
- Chapter 3- Rational Numbers
- Chapter 4- Exponents and Powers
- Chapter 5- Sets
- Chapter 6- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 7- Percentage and Its Applications
- Chapter 8- Algebraic Expressions
- Chapter 9- Linear Equations and Inequalitie
- Chapter 10- Lines and Angles
- Chapter 11- Triangles and its Properties
- Chapter 12- Congruence of Triangles
- Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
- Chapter 14- Symmetry
- Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes
- Chapter 16- Perimeter and Area
- Chapter 17- Data Handling
About ML Aggarwal
M. L. Aggarwal, is an Indian mechanical engineer, educator. His achievements include research in solutions of industrial problems related to fatigue design. Recipient Best Paper award, Manipal Institute of Technology, 2004. Member of TSTE.
