Class 12: Physics Chapter 15 solutions. Complete Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Notes.
Contents
NCERT Solutions for 12th Class Physics: Chapter 15-Communication Systems
NCERT 12th Physics Chapter 15, Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 solutions
Question 1.
Which of the following frequencies will be suit-able for beyond-the-horizon communication using sky waves?
(a) 10 kHz
(b) 10 MHz
(c) 1 GHz
(d) 1000 GHz
Solution:
(b) : 10 MHz will be suitable frequency for sky waves as lower frequency of 10 kHz will require large radiating antenna and higher frequencies 1 GHz and 1000 GHz will pass through the ionosphere and will not be reflected by it.
Question 2.
Frequencies in the UHF range normally propagate by means of:
(a) Ground waves
(b) Sky waves
(c) Surface waves
(d) Space waves
Solution:
(d) : Frequencies in the UHF range normally propagates by means of space waves. The high frequency space waves are ideal for frequency modulation but do not bend with ground.
Question 3.
Digital signals
(i) do not provide a continuous set of values,
(ii) represent values as discrete steps,
(iii) can utilize binary system, and
(iv) can utilize decimal as well as binary systems.
Which of the above statements are true?
(a) (i) and (ii) only
(b) (ii) and (iii) only
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) but not (iv)
(d) All of (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv).
Solution:
(c) : Decimal system represents a continuous set of values which cannot be utilized by digital signals.
Question 4.
Is it necessary for a transmitting antenna to be at the same height as that of the receiving antenna for the line of sight communication? A TV transmitting antenna is 81 m tall. How much service area can it cover if the receiving antenna is at the ground level?
Solution:
No, for line of sight communication, the two antenna may not be at the same height. Surface area
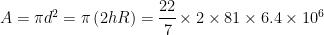
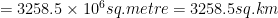
Question 5.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 12 V is used to transmit a message signal. What should be the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to have a modulation index of 75%?
Solution:
Modulation index,
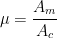
so, peak voltage
Question 6.
A modulating signal is a square wave, as shown in Figure
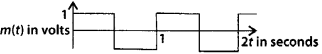
The carrier wave is given by c(t) = 2sin (8πt) volts
(i) Sketch the amplitude modulated wave form
(ii) What is the modulation index?
Solution:
(i) The amplitude modulated wave is shown here’:
(ii) Modulation index,

Question 7.
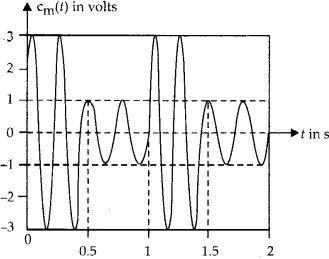
For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is found to be 10 V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 2 V. Determine the modulation index, p. What would be the value of p if the minimum amplitude is zero volt?
Solution:
We know
Modulation index,
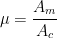
Also, minimum amplitude,

Maximum amplitude,

So, modulation index,
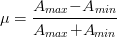
or
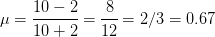
if Amin = O, then modulation index,
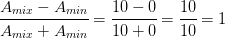
Question 8.
Due to economic reasons, only the upper side band of an AM wave is transmitted, but at the receiving station, there is a facility for generating the carrier. Show that if a device is available which can multiply two signals, then it is possible to recover the modulating signal at the receiver station.
Solution:
Let, the received signal be cos(ωc + ωm)t The carrier signal available at the receiving station is Ac cos ωct Multiplying the two signals, we get A1Ac cos (ωc + ωm)t cos ωct
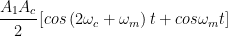
If this signal is passed through a low pass filter, we can recover the modulating signal
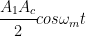
NCERT Solutions for 12th Class Physics: Chapter 1: Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for 12th Class Physics: Chapter 1-Electric Charges And Fields
Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for 12th Class Physics: Chapter 1-Electric Charges And Fields PDF
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics :
- Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields
- Chapter-2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Chapter 3: Current Electricity
- Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism
- Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter
- Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction
- Chapter 7: Alternating Current
- Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
- Chapter 9: Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- Chapter 10: Wave Optics
- Chapter 11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
- Chapter 12: Atoms
- Chapter 13: Nuclei
- Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuit
- Chapter 15: Communication Systems
About NCERT
The National Council of Educational Research and Training is an autonomous organization of the Government of India which was established in 1961 as a literary, scientific, and charitable Society under the Societies Registration Act. Its headquarters are located at Sri Aurbindo Marg in New Delhi. Visit the Official NCERT website to learn more.
