Class 6: Maths Chapter 13 solutions. Complete Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Notes.
Contents
ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
ML Aggarwal 6th Maths Chapter 13, Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 solutions
1. Construct a circle of radius:
(i) 2 cm
(ii) 3.5 cm
Solution:-
(i) From the question it is given that radius of circle is 2 cm.
Steps to construct a circle,
(a) Draw 2 cm line OA by using ruler.
(b) Then keeping the compass opened for the same length.
(c) Keep the pointer on O.
(d) Draw a circle using the pencil end of the compass.
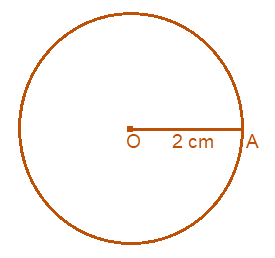
Therefore, this is the required circle of radius 2 cm.
(ii) From the question it is given that radius of circle is 3.5 cm.
Steps to construct a circle,
(a) Draw 3.5 cm line OA by using ruler.
(b) Then keeping the compass opened for the same length.
(c) Keep the pointer on O.
(d) Draw a circle using the pencil end of the compass.
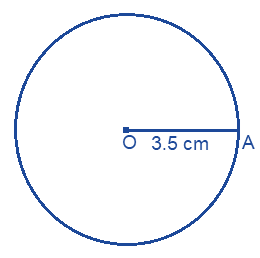
Therefore, this is the required circle of radius 3.5 cm.
2. With the same center O, draw two circles of radii 2.6 cm and 4.1 cm.
Solution:-
As per the condition given in the question, with the same center O, draw two circles of radii 2.6 cm and 4.1 cm
Steps to construct a circle,
(a) Mark a point O.
(b) Then keeping the compass opened for the length 2.6 cm by using ruler.
(c) Keep the pointer on O.
(d) Draw a circle using the pencil end of the compass.
Again, at the same point O.
(b) keeping the compass opened for the length 4.1 cm by using ruler.
(c) Keep the pointer on O.
(d) Draw a circle using the pencil end of the compass.

Therefore, above figure is the required two circles at same point O of radius 2.6 cm and 4.1 cm.
3. Draw any circle and mark points A, B and C such that
(i) A is on the circle.
(ii) B is in the interior of the circle.
(iii) C is in the exterior of the circle
Solution:-
(i) A is on the circle.

(ii) B is in the interior of the circle.

(iii) C is in the exterior of the circle
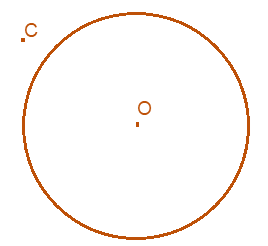
4. Draw a circle and any two of its (non-perpendicular) diameters. If you join the ends of these diameters, what is the figure obtained? What figure is obtained if the diameters are perpendicular to each other? How do you check your answer?
Solution:-
First we have to draw a circle and any two of its (non-perpendicular) diameters. Then joining the ends of the diameters, we get

Therefore, the obtained figure is rectangle.
Now, we have to draw a circle and the diameters are perpendicular to each other we get,
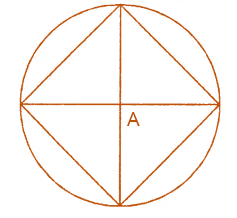
Therefore, the obtained figure is square.
5. Let A, B be the centers of two circles of equal radii; draw them so that each one of them passes through the center of the other. Let them intersect at C and D.
Examine whether and are at right angles.
Solution:-

By observing the figure we can say that, 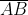 and
and 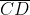 are at right angles.
are at right angles.
6. Construct a line segment of length of 6.3 cm using ruler and compass.
Solution:-
Let us assume P and Q are the two points.
Now, mark the two points by using the ruler 6.3 cm apart.
Then, join PQ we get,
 is a line segment of length 6.3 cm.
is a line segment of length 6.3 cm.

Download PDF
ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
Download PDF: ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13- Practical Geometry PDF
Chapterwise ML Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Maths :
- Chapter 1- Knowing Our Numbers
- Chapter 2- Whole Numbers
- Chapter 3- Integers
- Chapter 4- Playing with Numbers
- Chapter 5- Sets
- Chapter 6- Fractions
- Chapter 7- Decimals
- Chapter 8- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 9- Algebra
- Chapter 10- Basic Geometrical Concept
- Chapter 11- Understanding Symmetrical Shapes
- Chapter 12- Symmetry
- Chapter 13- Practical Geometry
- Chapter 14- Mensuration
- Chapter 15- Data Handling
About ML Aggarwal
M. L. Aggarwal, is an Indian mechanical engineer, educator. His achievements include research in solutions of industrial problems related to fatigue design. Recipient Best Paper award, Manipal Institute of Technology, 2004. Member of TSTE.
