Class 9: Maths Chapter 3.2 solutions. Complete Class 9 Maths Chapter 3.2 Notes.
Contents
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 9-Maths (Part 1): Chapter 3.2- Polynomials
Maharashtra Board 9th Maths Chapter 3.2, Class 9 Maths Chapter 3.2 solutions
Question 1.
Divide each of the following polynomials by synthetic division method and also by linear division method. Write the quotient and the remainder.
i. (2m2 – 3m + 10) ÷ (m – 5)
ii. (x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5) ÷ (x + 2)
iii. (y3 – 216) ÷ (y – 6)
iv. (2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2) ÷ (x + 3)
v. (x4 – 3x2 – 8) ÷ (x + 4)
vi. (y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1) ÷ (y – 1)
Solution:
i. Synthetic division:
(2m2 – 3m + 10) ÷ (m – 5)
Dividend = 2m² – 3m + 10
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (2, -3, 10)
Divisor = m – 5
∴ Opposite of -5 is 5.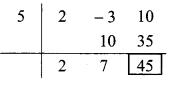
Coefficient form of quotient = (2, 7)
∴ Quotient = 2m + 7,
Remainder = 45
Linear division method:
2m2 – 3m + 10
To get the term 2m2, multiply (m – 5) by 2m and add 10m,
= 2m(m – 5) + 10m- 3m + 10
= 2m(m – 5) + 7m + 10
To get the term 7m, multiply (m – 5) by 7 and add 35
= 2m(m – 5) + 7(m- 5) + 35+ 10
= (m – 5) (2m + 7) + 45
∴ Quotient = 2m + 7,
Remainder = 45
ii. Synthetic division:
(x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5) ÷ (x + 2)
Dividend = x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
Divisor = x + 2
∴ Opposite of + 2 is -2.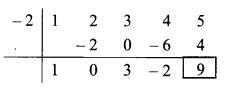
Coefficient form of quotient = (1, 0, 3, -2)
∴ Quotient = x3 + 3x – 2,
Remainder = 9
Linear division method:
x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
To get the term x4, multiply (x + 2) by x3 and subtract 2x3,
= x3(x + 2) – 2x3 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x2 + 4x + 5
To get the term 3x2, multiply (x + 2) by 3x and subtract 6x,
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 6x + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 2x + 5
To get the term -2x, multiply (x + 2) by -2 and add 4,
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 2(x + 2) + 4 + 5
= (x + 2) (x3 + 3x – 2) + 9
∴ Quotient = x3 + 3x – 2,
Remainder – 9
iii. Synthetic division:
(y3 – 216) ÷ (y – 6)
Dividend = y3 – 216
∴ Index form = y3 + 0y3 + 0y – 216
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (1, 0, 0, -216)
Divisor = y – 6
∴ Opposite of – 6 is 6.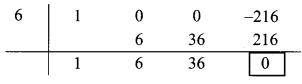
Coefficient form of quotient = (1, 6, 36)
∴ Quotient = y2 + 6y + 36,
Remainder = 0
Linear division method:
y3 – 216
To get the term y3, multiply (y – 6) by y2 and add 6y2,
= y2(y – 6) + 6y2 – 216
= y2(y – 6) + 6ysup>2 – 216
To get the, term 6 y2 multiply (y – 6) by 6y and add 36y,
= y2(y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36y – 216
= y2(y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36y – 216
To get the term 36y, multiply (y- 6) by 36 and add 216,
= y2 (y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36(y – 6) + 216 – 216
= (y – 6) (y2 + 6y + 36) + 0
Quotient = y2 + 6y + 36
Remainder = 0
iv. Synthetic division:
(2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2) ÷ (x + 3)
Dividend = 2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2
∴ Index form = 2x4 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x + 0
∴ Coefficient form of the dividend = (2,3, -2,4,0)
Divisor = x + 3
∴ Opposite of + 3 is -3
Coefficient form of quotient = (2, -3, 7, -17)
∴ Quotient = 2x3 – 3x2 + 7x – 17,
Remainder = 51
Linear division method:
2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2 = 2x2 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
To get the term 2x4, multiply (x + 3) by 2x3 and subtract 6x3,
= 2x3(x + 31 – 6x3 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
To get the term – 3x3, multiply (x + 3) by -3x2 and add 9x2,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 9x2 – 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x2 + 4x
To get the term 7x2, multiply (x + 3) by 7x and subtract 21x,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) – 21x + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) – 17x
To get the term -17x, multiply (x + 3) by -17 and add 51,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x+3) – 17(x + 3) + 51
= (x + 3) (2x3 – 3x2 + 7x- 17) + 51
∴ Quotient = 2x3 – 3x2 + 7x – 17,
Remainder = 51
v. Synthetic division:
(x4 – 3x2 – 8) + (x + 4)
Dividend = x4 – 3x2 – 8
∴ Index form = x4 + 0x3 – 3x2 + 0x – 8
∴ Coefficient form of the dividend = (1,0, -3,0, -8)
Divisor = x + 4
∴ Opposite of + 4 is -4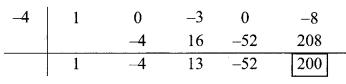
∴ Coefficient form of quotient = (1, -4, 13, -52)
∴ Quotient = x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52,
Remainder = 200
Linear division method:
x4 – 3x2 – 8
To get the term x4, multiply (x + 4) by x3 and subtract 4x3,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x3 – 3x2 – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x3 – 3x2 – 8
To get the term – 4x3, multiply (x + 4) by -4x2 and add 16x2,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2 (x + 4) + 16x2 – 3x2 – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2 (x + 4) + 13x2 – 8
To get the term 13x2, multiply (x + 4) by 13x and subtract 52x,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52x – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52x – 8
To get the term -52x, multiply (x + 4) by – 52 and add 208,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52(x + 4) + 208 – 8
= (x + 4) (x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52) + 200
∴ Quotient = x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52,
Remainder 200
vi. Synthetic division:
(y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1) ÷ (y – 1)
Dividend = y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1
Coefficient form of the dividend = (1, -3, 5, -1)
Divisor = y – 1
∴Opposite of -1 is 1.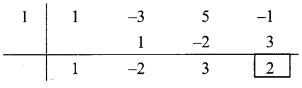
∴ Coefficient form of quotient = (1, -2, 3)
∴ Quotient = y2 – 2y + 3,
Remainder = 2
Linear division method:
y3 -3y2 + 5y – 1
To get the term y3 , multiply (y – 1) by y2 and add y2
= y2 (y – 1) + y2 – 3y2 + 5y – 1
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y2 + 5y – 1
To get the term -2y2, multiply (y – 1) by -2y and subtract 2y,
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) – 2y + 5y – 1
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) + 3y – 1
To get the term 3y, multiply (y – 1) by 3 and add 3,
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) + 3(y- 1) + 3 – 1
= (y – 1)(y2 – 2y + 3) + 2
∴ Quotient = y2 – 2y + 3,
Remainder = 2.
Download PDF
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 9-Maths (Part 1): Chapter 3.2- Polynomials
Download PDF: Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 9-Maths (Part 1): Chapter 3.2- Polynomials PDF
Chapterwise Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 9 Maths :
Part 1
- Chapter 1.1- Sets
- Chapter 1.2- Sets
- Chapter 1.3- Sets
- Chapter 1.4- Sets
- Chapter 2.1- Real Numbers
- Chapter 2.2- Real Numbers
- Chapter 2.3- Real Numbers
- Chapter 2.4- Real Numbers
- Chapter 2.5- Real Numbers
- Chapter 3.1- Polynomials
- Chapter 3.2- Polynomials
- Chapter 3.3- Polynomials
- Chapter 3.4- Polynomials
- Chapter 3.5- Polynomials
- Chapter 3.6- Polynomials
- Chapter 4.1- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 4.2- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 4.3- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 4.4- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 4.5- Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 5.1- Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 5.2- Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 6.1- Financial Planning
- Chapter 6.2- Financial Planning
- Chapter 7.1- Statistics
- Chapter 7.2- Statistics
- Chapter 7.3- Statistics
- Chapter 7.4- Statistics
- Chapter 7.5- Statistics
FAQs
You can download the Maharashtra State Board Books from the eBalbharti official website, i.e. cart.ebalbharati.in or from this article.
Students can get the Maharashtra Books for primary, secondary, and senior secondary classes from here. You can view or download the Maharashtra State Board Books from this page or from the official website for free of cost. Students can follow the detailed steps below to visit the official website and download the e-books for all subjects or a specific subject in different mediums.
Step 1: Visit the official website ebalbharati.in
Step 2: On the top of the screen, select “Download PDF textbooks”
Step 3: From the “Classes” section, select your class.
Step 4: From “Medium”, select the medium suitable to you.
Step 5: All Maharashtra board books for your class will now be displayed on the right side.
Step 6: Click on the “Download” option to download the PDF book.
As of now, the MSCERT and Balbharti are responsible for the syllabus and textbooks of Classes 1 to 8, while Classes 9 and 10 are under the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE).
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education, conducts the HSC and SSC Examinations in the state of Maharashtra through its nine Divisional Boards located at Pune, Mumbai, Aurangabad, Nasik, Kolhapur, Amravati, Latur, Nagpur and Ratnagiri.
About Maharashtra State Board (MSBSHSE)
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education or MSBSHSE (Marathi: महाराष्ट्र राज्य माध्यमिक आणि उच्च माध्यमिक शिक्षण मंडळ), is an autonomous and statutory body established in 1965. The board was amended in the year 1977 under the provisions of the Maharashtra Act No. 41 of 1965.
The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education (MSBSHSE), Pune is an independent body of the Maharashtra Government. There are more than 1.4 million students that appear in the examination every year. The Maha State Board conducts the board examination twice a year. This board conducts the examination for SSC and HSC.
The Maharashtra government established the Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, also commonly referred to as Ebalbharati, in 1967 to take up the responsibility of providing quality textbooks to students from all classes studying under the Maharashtra State Board. MSBHSE prepares and updates the curriculum to provide holistic development for students. It is designed to tackle the difficulty in understanding the concepts with simple language with simple illustrations. Every year around 10 lakh students are enrolled in schools that are affiliated with the Maharashtra State Board.
