NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles prepare students for their Class 9 exams thoroughly.
Maths problems and solutions for the Class 9 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
Contents
- 1 NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- 1.1 Main Concepts and Results
- 1.2 Multiple Choice Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.3 Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
- 1.4 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Solved Examples)
- 1.5 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)
- 1.6 Short Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.7 Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
- 1.8 Long Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.9 Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
- 1.10 Answers
- 1.11 Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
- 1.12 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)
- 1.13 Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
Class 9: Maths Chapter 9 solutions. Complete Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Notes.
Main Concepts and Results
The area of a closed plane figure is the measure of the region inside the figure:
The shaded parts (Fig.9.1) represent the regions whose areas may be determined by means of simple geometrical results. The square unit is the standard unit used in measuring the area of such figures.
- If ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ PQR, then ar (∆ ABC) = ar (∆ PQR)
Total area R of the plane figure ABCD is the sum of the areas of two triangular regions R 1 and R 2 , that is, ar (R) = ar (R 1 ) + ar (R 2 )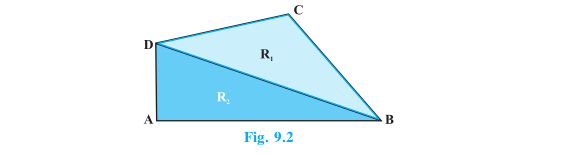
- Two congruent figures have equal areas but the converse is not always true,
- A diagonal of a parallelogram divides the parallelogram in two triangles of equal area,
- (i) Parallelograms on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area
(ii) A parallelogram and a rectangle on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area. - Parallelograms on equal bases and between the same parallels are equal in area,
- Triangles on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area,
- Triangles with equal bases and equal areas have equal corresponding altitudes,
- The area of a triangle is equal to one-half of the area of a rectangle/parallelogram of the same base and between same parallels,
- If a triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between the same parallels, the area of the triangle is equal to one-half area of the parallelogram.
Multiple Choice Questions (Solved Examples)

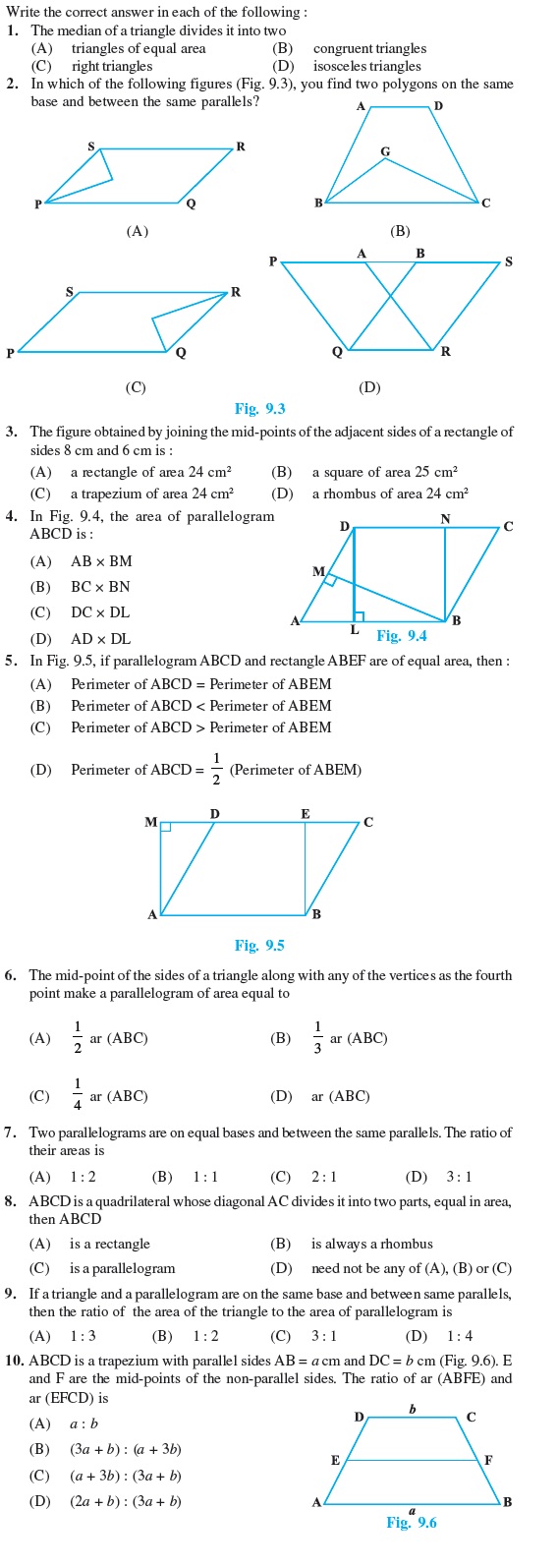
Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Solved Examples)


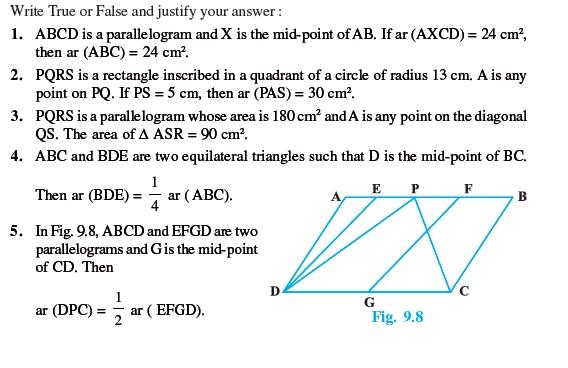
Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)
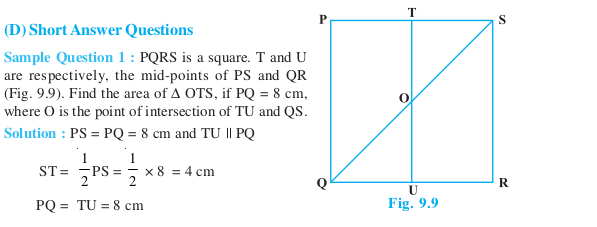
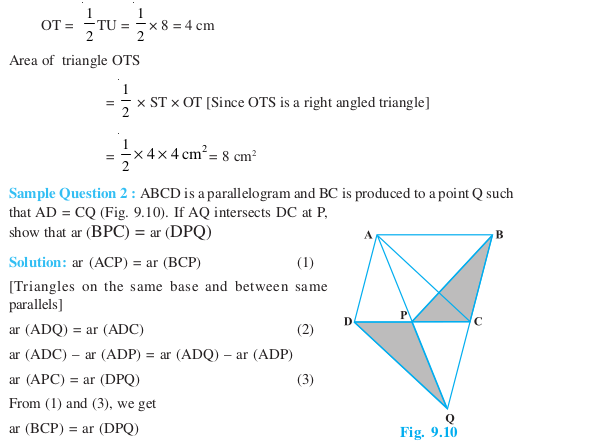
Short Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
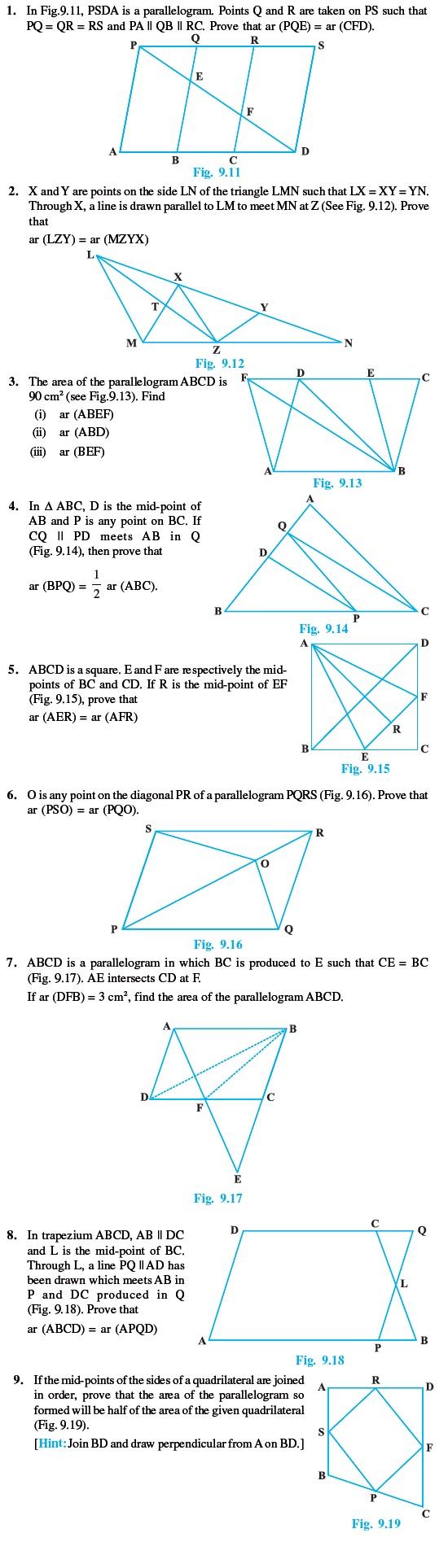
Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
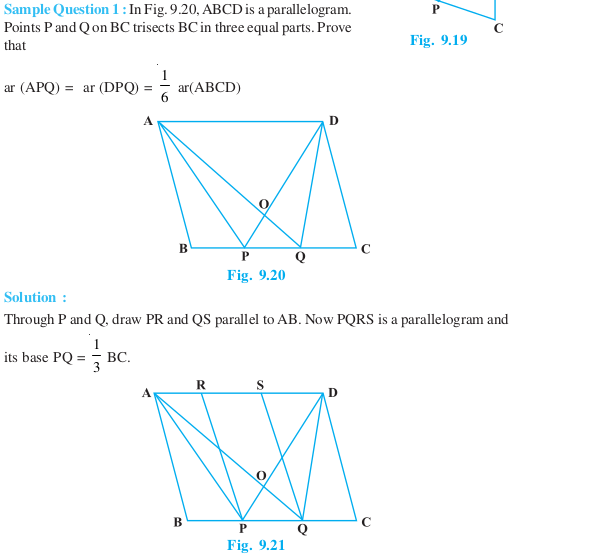
Long Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
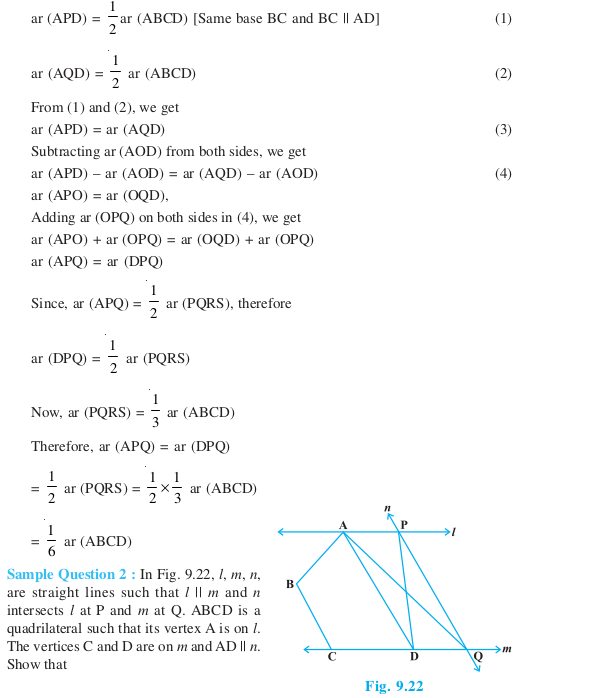
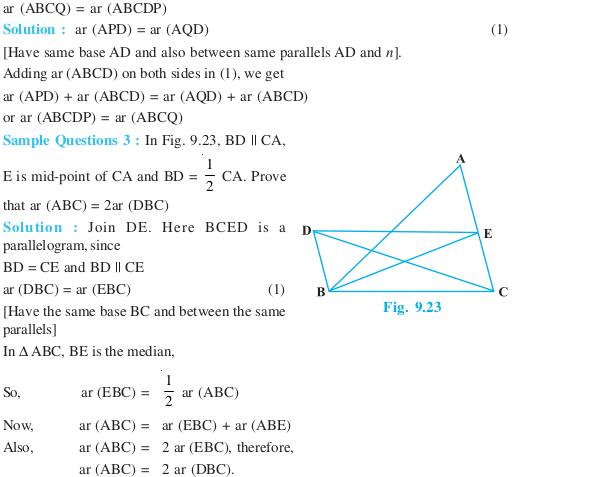
Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
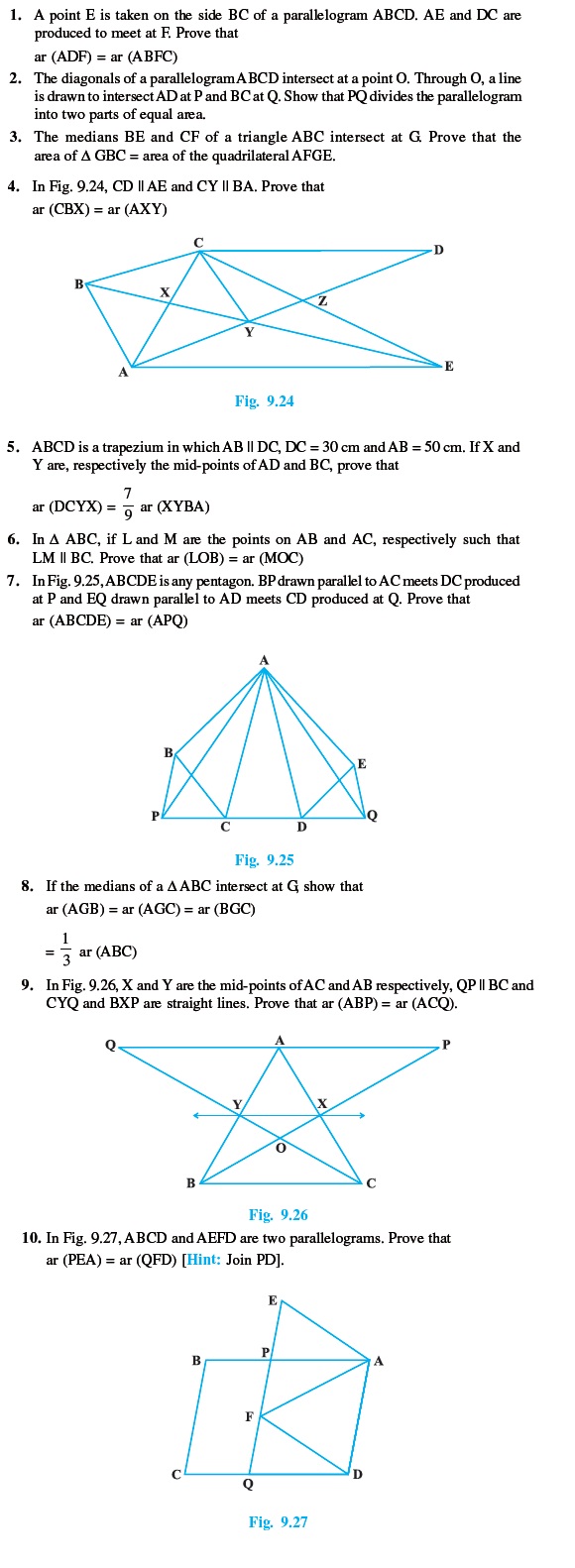
Answers
Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)

Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)

