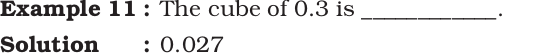NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root prepare students for their Class 8 exams thoroughly.
Maths problems and solutions for the Class 8 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
Contents
- 1 NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
- 1.1 Main Concepts and Results
- 1.2 Key Notes
- 1.3 Think and Discuss
- 1.4 Solved Examples
- 1.5
- 1.6 Fill in the Blanks
- 1.7
- 1.8
- 1.9 Connect
- 1.10 Statements are true (T) or false (F)
- 1.11
- 1.12
- 1.13
- 1.14
- 1.15 Connet
- 1.16
- 1.17
- 1.18 Think and Discuss
- 1.19
- 1.20
- 1.21
- 1.22 Think and Discuss
- 1.23
- 1.24
- 1.25
- 1.26
- 1.27 Multiple Choice Questions
- 1.28 Answers to Multiple Choice Questions
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
Class 8: Maths Chapter 3 solutions. Complete Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Notes.
Main Concepts and Results
- A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n2, then m is a perfect square where m and n are natural numbers.
- A natural number is called a perfect cube if it is the cube of some natural number. i.e., if m = n3, then m is a perfect cube where m and n are natural numbers
- Number obtained when a number is multiplied by itself is called the square of the number.
- Number obtained when a number is multiplied by itself three times are called cube number cube number.
- Squares and cubes of even numbers are even and Squares and cubes of odd numbers are odd.
- A perfect square can always be expressed as the product of pairs of prime factors.
- A perfect cube can always be expressed as the product of triplets of prime factors.
- The unit digit of a perfect square can be only 0, 1, 4, 5, 6 or 9.
- The square of a number having:
- 1 or 9 at the units place ends in1.
- 2 or 8 at the units place ends in 4.
- 3 or 7 at the units place ends in 9.
- 4 or 6 at the units place ends in 6.
- 5 at the units place ends in 5.
- There are 2n natural numbers between the squares of numbers n and n+1.
- A number ending in odd numbers of zeroes is not a perfect square.
- The sum of first n odd natural numbers is given by n2
- Three natural numbers a, b, c are said to form a pythagorean triplet if a2 + b2 = c2.
- For every natural number m > 1, 2m, m2–1 and m2 + 1 form a pythagorean triplet.
- The square root of a number x is the number whose square is x. Positive square root of a number x is denoted by x .
- The cube root of a number x is the number whose cube is x. It is denoted by 3 x .
- Square root and cube root are the inverse operations of squares and cubes respectively.
- If a perfect square is of n digits, then its square root will have n/2 digit if n is even or
 digit if n is odd.
digit if n is odd.- Cubes of the numbers ending with the digits 0, 1, 4, 5, 6 and 9 end with digits 0, 1, 4, 5, 6 and 9 respectively.
Key Notes
SQUARE ROOTS
Words A square root of a number n is a number m which, when multiplied by itself, equals n.
Numbers The square roots of 16 are 4 and – 4 because 42 = 16 and (– 4)2 = 16.
Algebra If m2 = n, then m is a square root of n.
Think and Discuss
- Which type of number has an exact square root?
- Which type of number has an approximate square root?
- How can we use perfect squares to estimate a square root, such as √8 ?
⊳ Cube of the number ending in 2 ends in 8 and cube root of the number ending in 8 ends in 2.
⊳ Cube of the number ending in 3 ends in 7 and cube root of the number ending in 7 ends in 3.
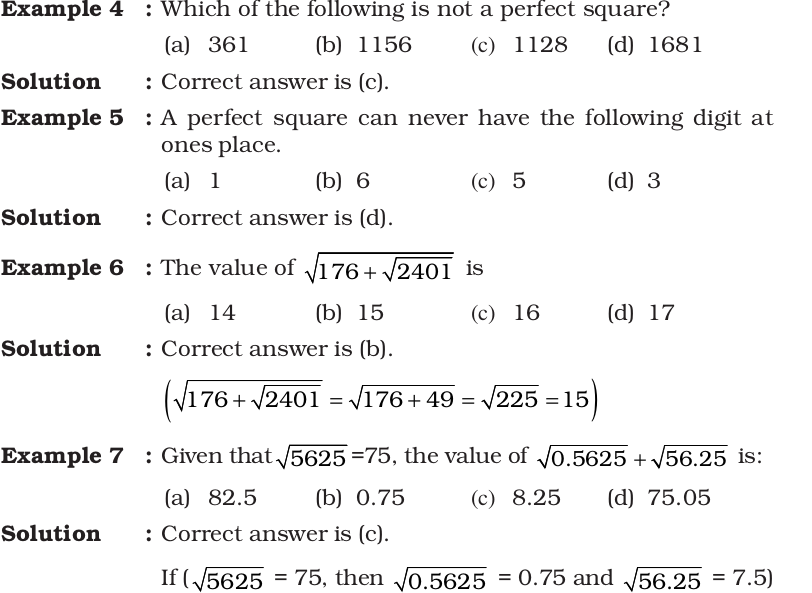
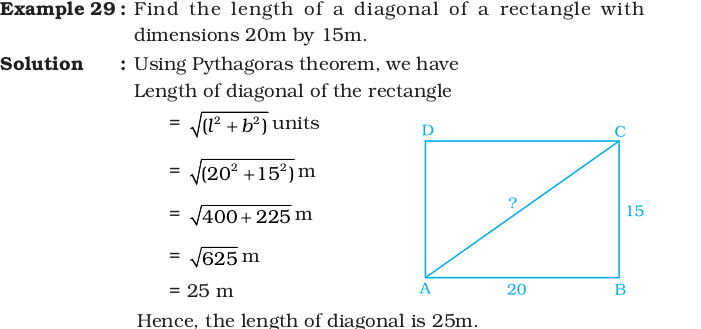
Solved Examples

Fill in the Blanks

Connect


Statements are true (T) or false (F)

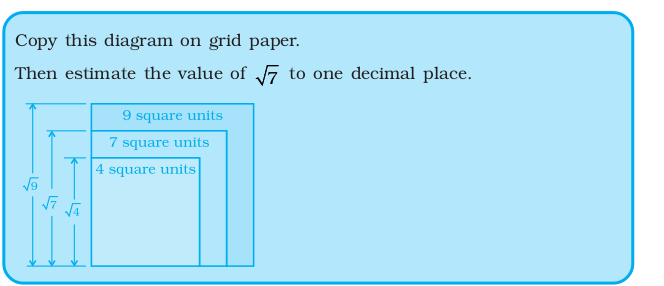
Connet
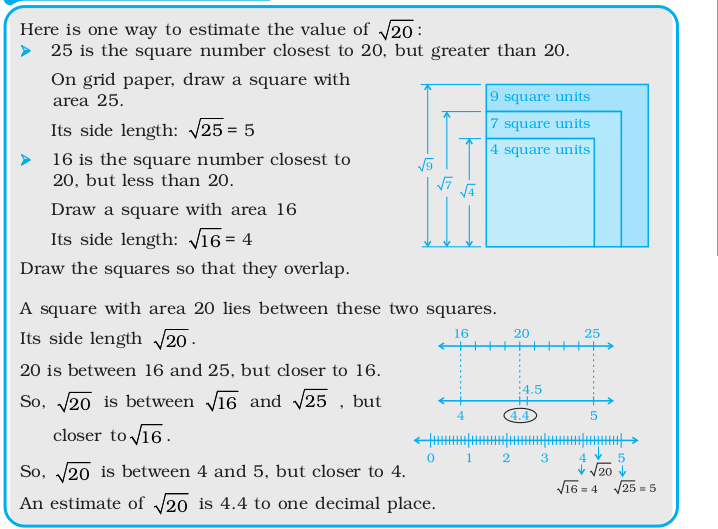
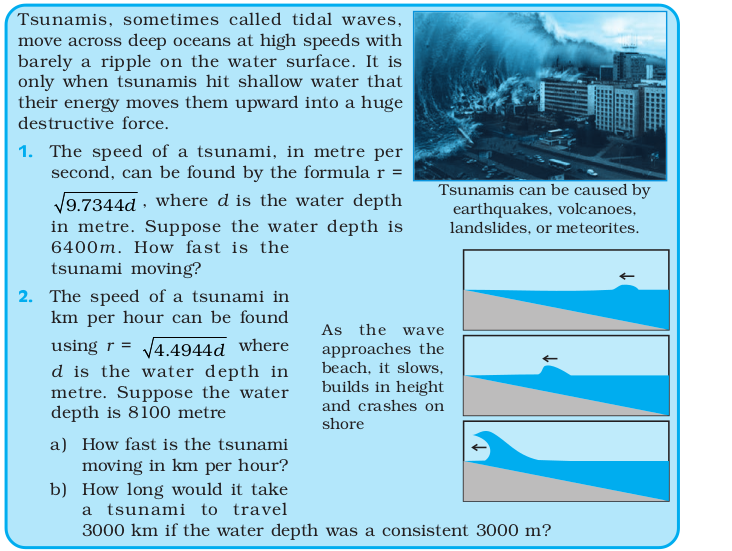
Think and Discuss
- Is 1 a square number? How can you tell?
- Suppose you know the area of a square. How can you find its perimeter?
- Suppose you know the perimeter of a square. How can you find its area?
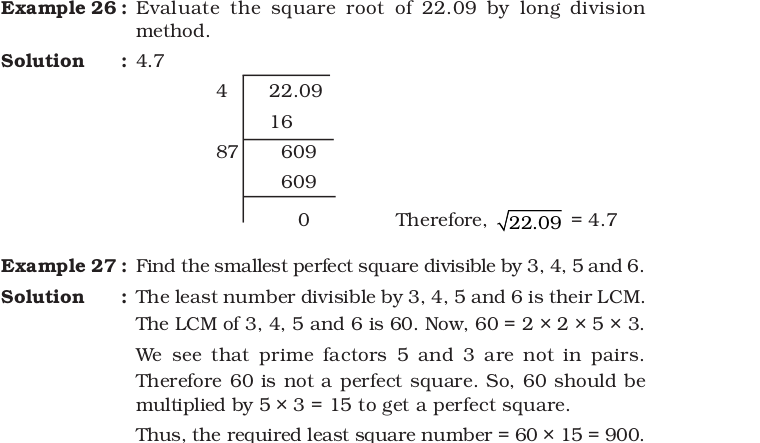
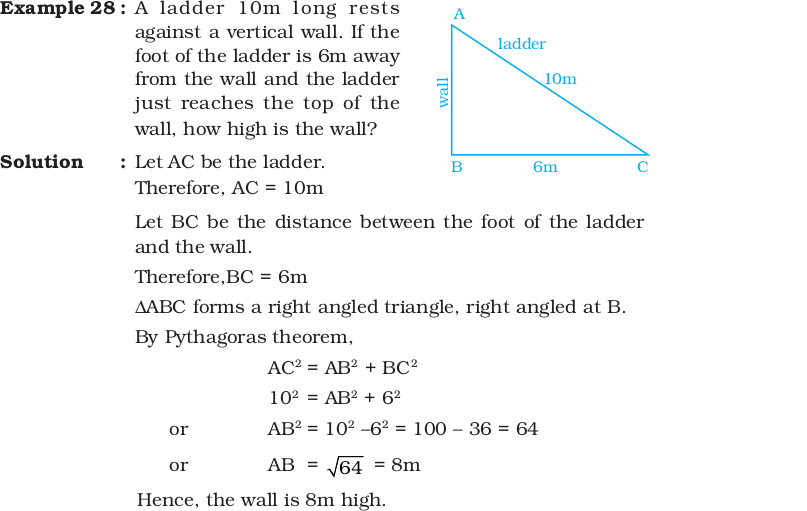
Think and Discuss
- Compare your strategies and results with those of another pair of
classmates. - Find two areas greater than 20 square units for which you could use tiles
to make a square - How do you know you could make a square for each of these areas?

Multiple Choice Questions

Fill in the Blanks Type Questions

True False Type Questions

Short Answer Type Questions

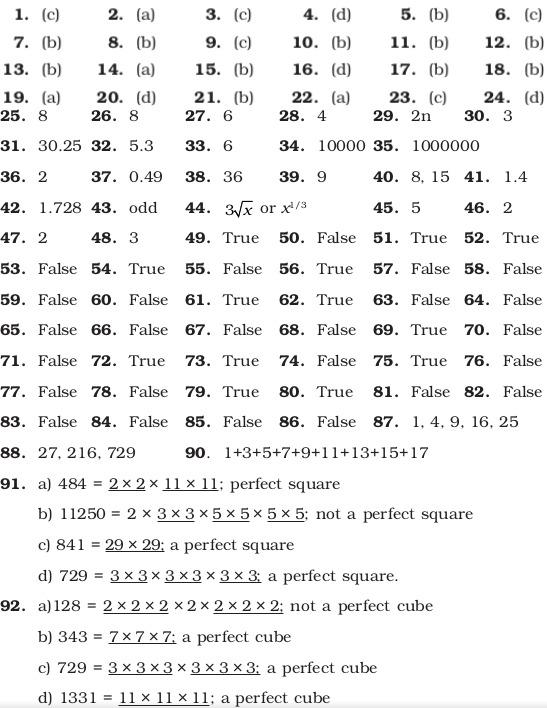
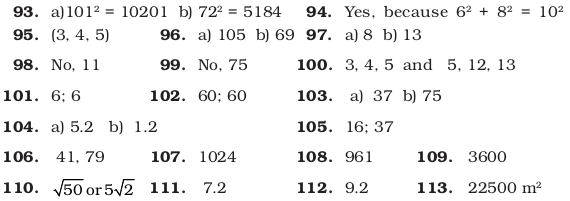
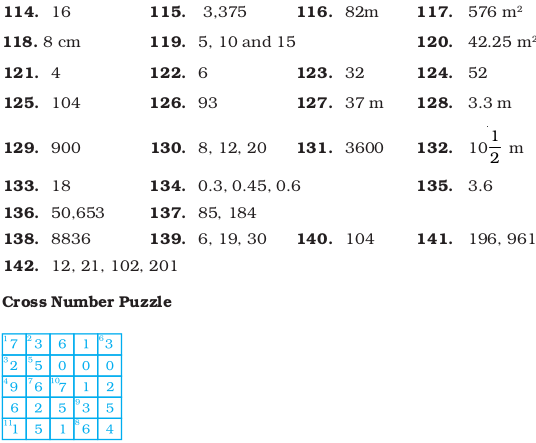
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions