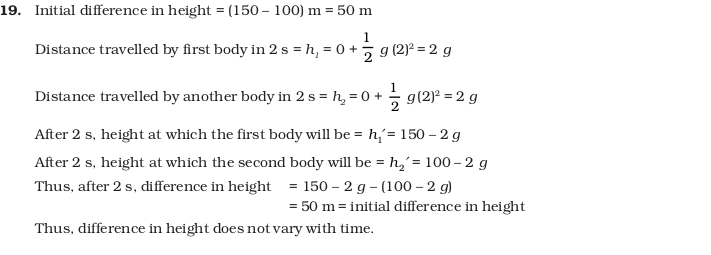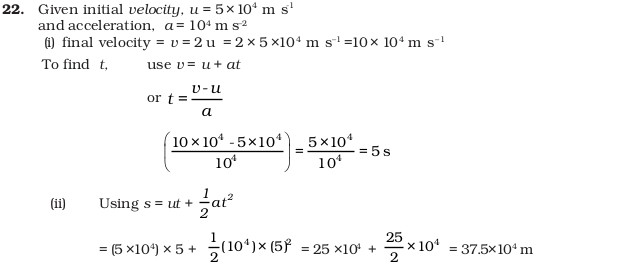NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 8: Motion. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion prepare students for their Class 9 exams thoroughly.
Science problems and solutions for the Class 9 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 8: Motion
Class 9: Science Chapter 8 solutions. Complete Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Notes.
Multiple Choice Questions
- A particle is moving in a circular path of radius r. The displacement after half a circle would be:
- (a) Zero
- (b) p r
- (c) 2 r
- (d) 2p r
- A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise is,
- (a) u/g
- (b) u2/2g
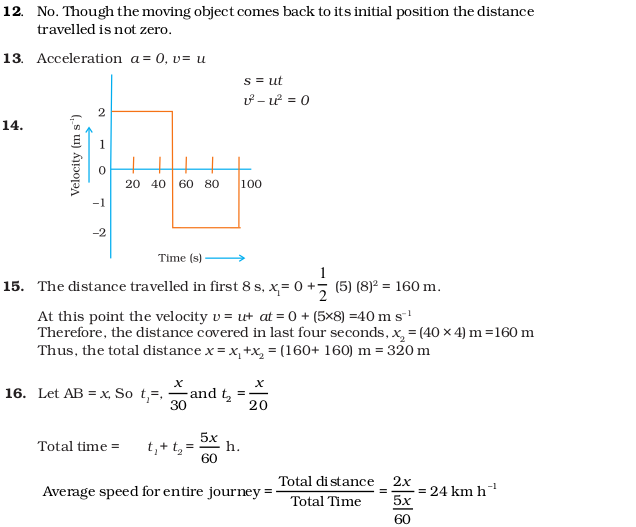
- (c) u2/g
- (d) u/2g
- The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is
- (a) always less than 1
- (b) always equal to 1
- (c) always more than 1
- (d) equal or less than 1
- If the displacement of an object is proportional to square of time, then the object moves with
- (a) uniform velocity
- (b) uniform acceleration
- (c) increasing acceleration
- (d) decreasing acceleration
- From the given v – t graph (Fig. 8.1), it can be inferred that the object is
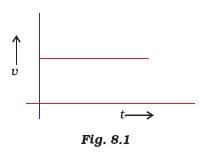
- (a) in uniform motion
- (b) at rest
- (c) in non-uniform motion
- (d) moving with uniform acceleration
- Suppose a boy is enjoying a ride on a merry-go-round which is moving with a constant speed of 10 m s–1. It implies that the boy is
- (a) at rest
- (b) moving with no acceleration
- (c) in accelerated motion
- (d) moving with uniform velocity
- Area under a v – t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit
- (a) m2
- (b) m
- (c) m3
- (d) m s-1
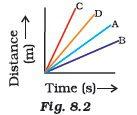
- Four cars A, B, C and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in Fig. 8.2. Choose the correct statement
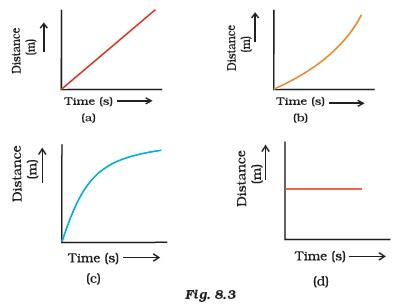
- Which of the following figures (Fig. 8.3) represents uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
- Slope of a velocity – time graph gives
- (a) the distance
- (b) the displacement
- (c) the acceleration
- (d) the speed
- In which of the following cases of motions, the distance moved and the magnitude of displacement are equal?
- (a) If the car is moving on straight road
- (b) If the car is moving in circular path
- (c) The pendulum is moving to and fro
- (d) The earth is revolving around the Sun
Short Answer Type Questions
- The displacement of a moving object in a given interval of time is zero. Would the distance travelled by the object also be zero? Justify you answer.
- How will the equations of motion for an object moving with a uniform velocity change?
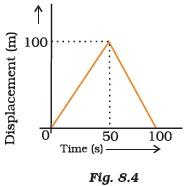
- A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement–time graph is shown in Fig.8.4. Plot a velocity–time graph for the same.
- A car starts from rest and moves along the x-axis with constant acceleration 5 m s–2 for 8 seconds. If it then continues with constant velocity, what distance will the car cover in 12 seconds since it started from the rest?
- A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h–1 and returns back with a speed of 20 km h–1. Find its average speed.
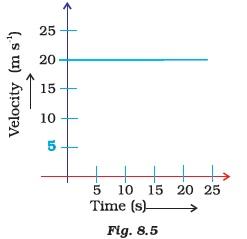
- The velocity-time graph (Fig. 8.5) shows the motion of a cyclist. Find (i) its acceleration (ii) its velocity and (iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds.
- Draw a velocity versus time graph of a stone thrown vertically upwards and then coming downwards after attaining the maximum height.
Long Answer Type Questions
- An object is dropped from rest at a height of 150 m and simultaneously another object is dropped from rest at a height 100 m. What is the difference in their heights after 2 s if both the objects drop with same accelerations? How does the difference in heights vary with time?
- An object starting from rest travels 20 m in first 2 s and 160 m in next 4 s. What will be the velocity after 7 s from the start.
- Using following data, draw time – displacement graph for a moving object:
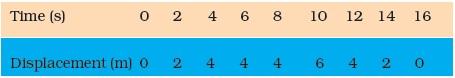
Use this graph to find average velocity for first 4 s, for next 4 s and for last 6 s. - An electron moving with a velocity of 5 × 104 m s-1 enters into a uniform electric field and acquires a uniform acceleration of 104 m s-2 in the direction of its initial motion.
- (i) Calculate the time in which the electron would acquire a velocity double of its initial velocity.
- (ii) How much distance the electron would cover in this time?
- Obtain a relation for the distance travelled by an object moving with a uniform acceleration in the interval between 4th and 5th seconds.
- Two stones are thrown vertically upwards simultaneously with their initial velocities u1 and u2 respectively. Prove that the heights reached by them would be in the ratio of u21 : u22 ( Assume upward acceleration is –g and downward acceleration to be +g ).
Answers