NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13: Motion and Time. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time prepare students for their Class 7 exams thoroughly.
Science problems and solutions for the Class 7 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
Contents
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13: Motion and Time
Class 7: Science Chapter 13 solutions. Complete Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Notes.
Multiple Choice Questions
- Which of the following cannot be used for measurement of time?
- (a) A leaking tap.
- (b) Simple pendulum.
- (c) Shadow of an object during the day.
- (d) Blinking of eyes.
- Two clocks A and B are shown in Figure 13.1. Clock A has an hour and a minute hand, whereas clock B has an hour hand, minute hand as well as a second hand. Which of the following statement is correct for these clocks?
- (a) A time interval of 30 seconds can be measured by clock A.
- (b) A time interval of 30 seconds cannot be measured by clock B.
- (c) Time interval of 5 minutes can be measured by both A and B.
- (d) Time interval of 4 minutes 10 seconds can be measured by clock A.
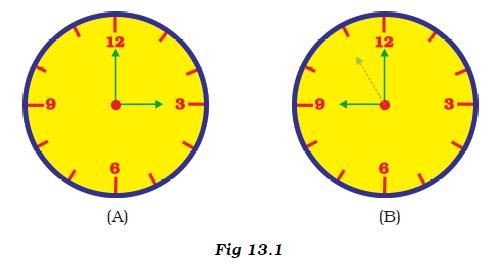
- Two students were asked to plot a distance-time graph for the motion described by Table A and Table B.
The graph given in Figure 13.2 is true for- (a) both A and B.
- (b) A only.
- (c) B only.
- (d) neither A nor B.
- A bus travels 54 km in 90 minutes. The speed of the bus is
- (a) 0.6 m/s
- (b) 10 m/s
- (c) 5.4 m/s
- (d) 3.6 m/s
- If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is
- (a) S = D × T
- (b) T = S / D
- (c) S = 1 / T * D
- (d) S = T / D
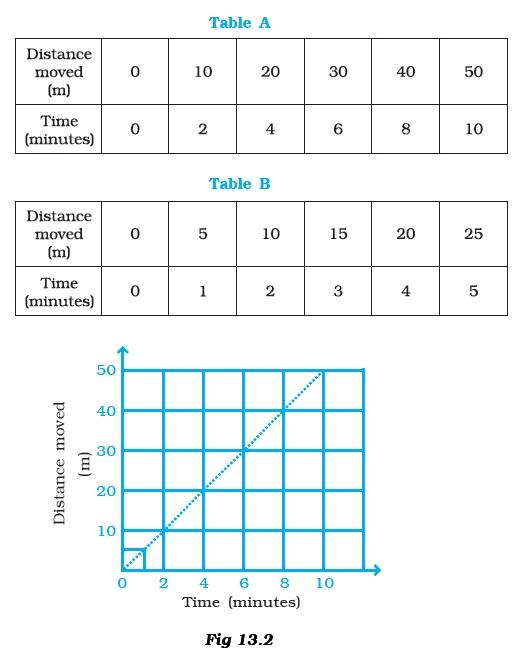
- Observe Figure 13.3.
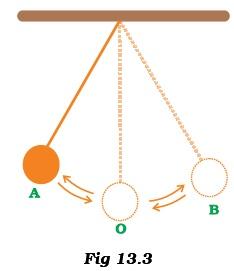
The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from- (a) A to B and back to A.
- (b) O to A, A to B and B to A.
- (c) B to A, A to B and B to O.
- (d) A to B.
- Fig. 13.4 shows an oscillating pendulum.

Time taken by the bob to move from A to C is t1 and from C to O is t2. The time period of this simple pendulum is- (a) (t1 + t2 )
- (b) 2 (t1 + t2 )
- (c) 3 (t1 + t2 )
- (d) 4 (t1 + t2 )
- The correct symbol to represent the speed of an object is
- (a) 5 m/s
- (b) 5 mp
- (c) 5 m/s-1
- (d) 5 s/m
- Boojho walks to his school which is at a distance of 3 km from his home in 30 minutes. On reaching he finds that the school is closed and comes back by a bicycle with his friend and reaches home in 20 minutes. His average speed in km/h is
- (a) 8.3
- (b) 7.2
- (c) 5
- (d) 3.6
Very Short Answer Type Questions
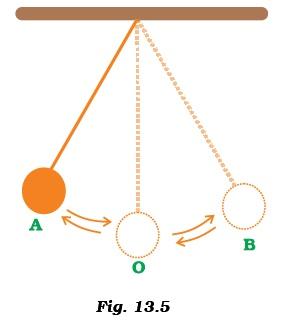
- A simple pendulum is oscillating between two points A and B as shown in Figure 13.5. Is the motion of the bob uniform or non-uniform?
- Paheli and Boojho have to cover different distances to reach their school but they take the same time to reach the school. What can you say about their speed?
- If Boojho covers a certain distance in one hour and Paheli covers the same distance in two hours, who travels in a higher speed?
Short Answer Type Questions
- Complete the data of the table given below with the help of the distance-time graph given in Figure 13.6.


- The average age of children of Class VII is 12 years and 3 months. Express this age in seconds.
- A spaceship travels 36,000 km in one hour. Express its speed in km/s.
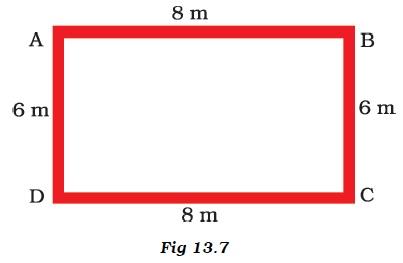
- Starting from A, Paheli moves along a rectangular path ABCD as shown in Figure 13.7. She takes 2 minutes to travel each side. Plot a distance-time graph and explain whether the motion is uniform or non-uniform.
- Plot a distance-time graph of the tip of the second hand of a clock by selecting 4 points on x-axis and y-axis respectively. The circumference of the circle traced by the second hand is 64 cm.
Long Answer Type Questions
- Given below as Figure 13.8 is the distance-time graph of the motion an object.
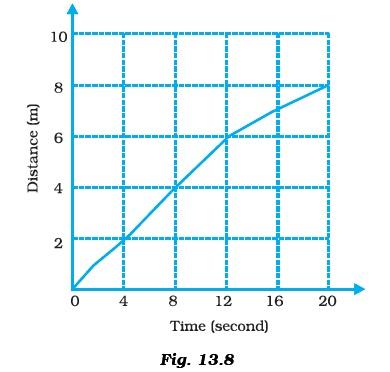
- (i) What will be the position of the object at 20s?
- (ii) What will be the distance travelled by the object in 12s?
- (iii) What is the average speed of the object?
- Distance between Bholu’s and Golu’s house is 9 km. Bholu has to attend Golu’s birthday party at 7 o’clock. He started from his home at 6 o’clock on his bicycle and covered a distance of 6 km in 40 minutes. At that point he met Chintu and he spoke to him for 5 minutes and reached Golu’s birthday party at 7 o’clock. With what speed did he cover the second part of the journey? Calculate his average speed for the entire journey.
- Boojho goes to the football ground to play football. The distance time graph of his journey from his home to the ground is given as Figure 13.9.

- (a) What does the graph between point B and C indicate about the motion of Boojho?
- (b) Is the motion between 0 to 4 minutes uniform or nonuniform?
- (c) What is his speed between 8 and 12 minutes of his journey?
Answers