Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Define provision. What is the important of creating a provision? (any three points of importance).
Solution 1: According to the companies Act the term ‘Provision’ refers to any of the following amounts:-
(i) The amount written off or retained by way of providing for depreciation, renewals or diminution in value of assets.
(ii) The amount retained by way of providing for any known liability of which the amount cannot be determined with substantial accuracy.
Below are the importance of provision:-
1.) To ascertain the true net profit of the business.
2.) To ascertain the true financial position of the business.
3.) To provide for known losses in the future.
Question 2. Give any four points of distinction between Provisions and Reserves.
Solution 2:
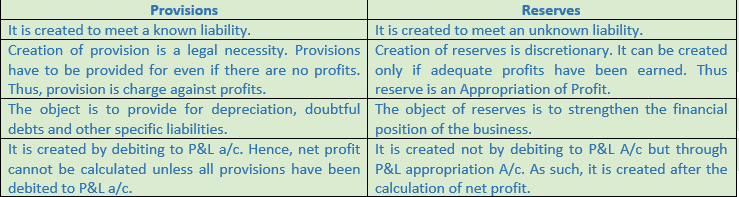
Question 3. Distinguish between Provision and Reserve on the following basis:
(i) Basic Nature
(ii) Purpose
(iii) Effect on Taxable Profits
(iv) Presentation in Balance Sheet
(v) Element of Compulsion
(vi) Use for payment of dividend.
Solution 3:
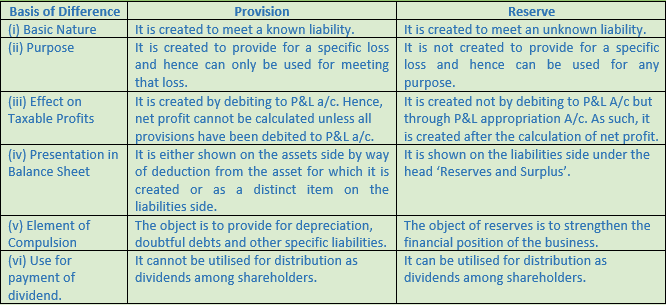
Question 4. Differentiate between Provision and Reserve on the basis of
(i) Appropriation or Charge
(ii) Financial Position
(iii) Distribution
Solution 4:
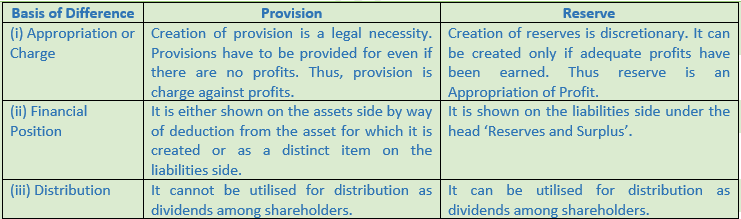
Question 5. Give five examples of Capital Reserve.
Solution 5: Below are the five examples of Capital Reserve:-
1.) Profit on the sales of fixed assets.
2.) Profit on the revolution of fixed assets and liabilities.
3.) Premiums received on issue of Shares or Debentures.
4.) Profit on the purchases of a running business.
5.) Profit prior to the incorporation of a company.
Question 6. Distinguish between Revenue Reserve and Capital Revenue.
Solution 6:
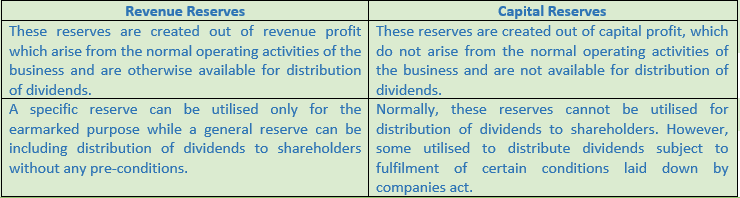
Question 7. Explain Capital Reserve and give its any two examples.
Solution 7: In the addition to the normal profit, capital profits are also earned in the business from many sources. The reserves created out of such capital profits are known as Capital Reserves.
Below are the five examples of Capital Reserve:-
1.) Profit on the sales of fixed assets.
2.) Profit on the revolution of fixed assets and liabilities.
Question 8. Write any three methods of creating secret reserves.
Solution 8: Secret reserves can be created in the following ways:
1.) Writing off excessive depreciation
2.) Charging Capital expenditure (such as addition to assets) to Profit and Loss Account.
3.) Treating a revenue receipt as a capital receipt (such as rent received credited to Building Account)
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. What are Provisions?
Solution 1: According to the companies Act the term ‘Provision’ refers to the amount written off or retained by way of providing for depreciation, renewals or diminution in value of assets.
Question 2. Give two examples of provisions.
Solution 2: Below are the examples of provisions:-
1.) Provision for Depreciation of Assets
2.) Provision for Taxation.
Question 3. What are Reserves?
Solution 3: Reserves mean amount set aside out of profit and other surpluses to meet future uncertainties. In other words a reserve is meant for meeting any unknown liability or loss in the future.
Question 4. Give two examples of reserves.
Solution 4: Below are the examples of reserves:-
1.) General Reserve
2.) Capital Reserve
Question 5. Give two differences between provisions and reserves.
Solution 5:
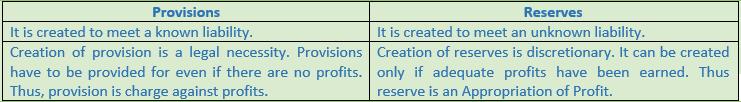
Question 6. Differentiate between reserve and provisions on the basis of change or appropriations.
Solution 6: Reserve is an appropriation of profit whereas provision is change against profit.
Question 7. Give one example of each of ‘provision’ and ‘reserve’.
Solution 7: Example for Provision:- Provision for Depreciation of Assets.
Example for Reserve:- General Reserve
Question 8. What is divided equalisation reserve?
Solution 8: Divided Equalisation Reserve is created to maintain steady rate of dividend. In the year in which the profits are sufficient, a part of the profit is transferred to such reserve and it is utilised to keep the dividend up in the year in which the profit are insufficient.
Question 9. What is Workmen Compensation Fund?
Solution 9: This fund created to meet compensation payable to workers in case of unexpected or unknown event of an accident.
Question 10. Give two examples of Specific Reserves.
Solution 10:
(i) Divide Equalisation Reserve
(ii) Workmen Compensation Fund
Question 11. What are Capital Reserves?
Solution 11 : In the addition to the normal profit, capital profits are also earned in the business from many sources. The reserves created out of such capital profits are known as Capital Reserves.
Question 12. Give one difference between General Reserve and Specific Reserve.
Solution 12:
General Reserve:- The businessman do not withdraw the entire profit from the business but retain a part of it in the business to meet unforeseen future and uncertainties.
Specific Reserve:- It is created for a specific purpose and can be utilised only for that purpose.
Question 13. Name the reserve that can be used in distribution of dividend.
Solution 13: Revenue Reserve can be used in distribution of dividend.
Question 14. Where will you transfer profit on sale of a fixed asset?
Solution 14: Profit on sale of a fixed asset is a capital profit and therefore it will be transferred to Capital Reserve.
