Contents
The syllabus for SAAT 2025 has been released by Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (deemed to be University) (SOA University). If you are gearing up for the Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan Admission Test, you can access and download the SAAT Syllabus PDF to aid your exam preparation. The syllabus for the SAAT exam outlines the subjects and topics that need to be studied for the entrance test. By thoroughly covering the exam syllabus and addressing other aspects of SAAT preparation, you can aspire to achieve a commendable score and rank in SAAT 2025.
SAAT Syllabus
SAAT 2025 Syllabus PDF Download Link – You can download the 2025 syllabus as per its issuance by SOA University at admission.soa.ac.in or here.























































SAAT Exam Pattern
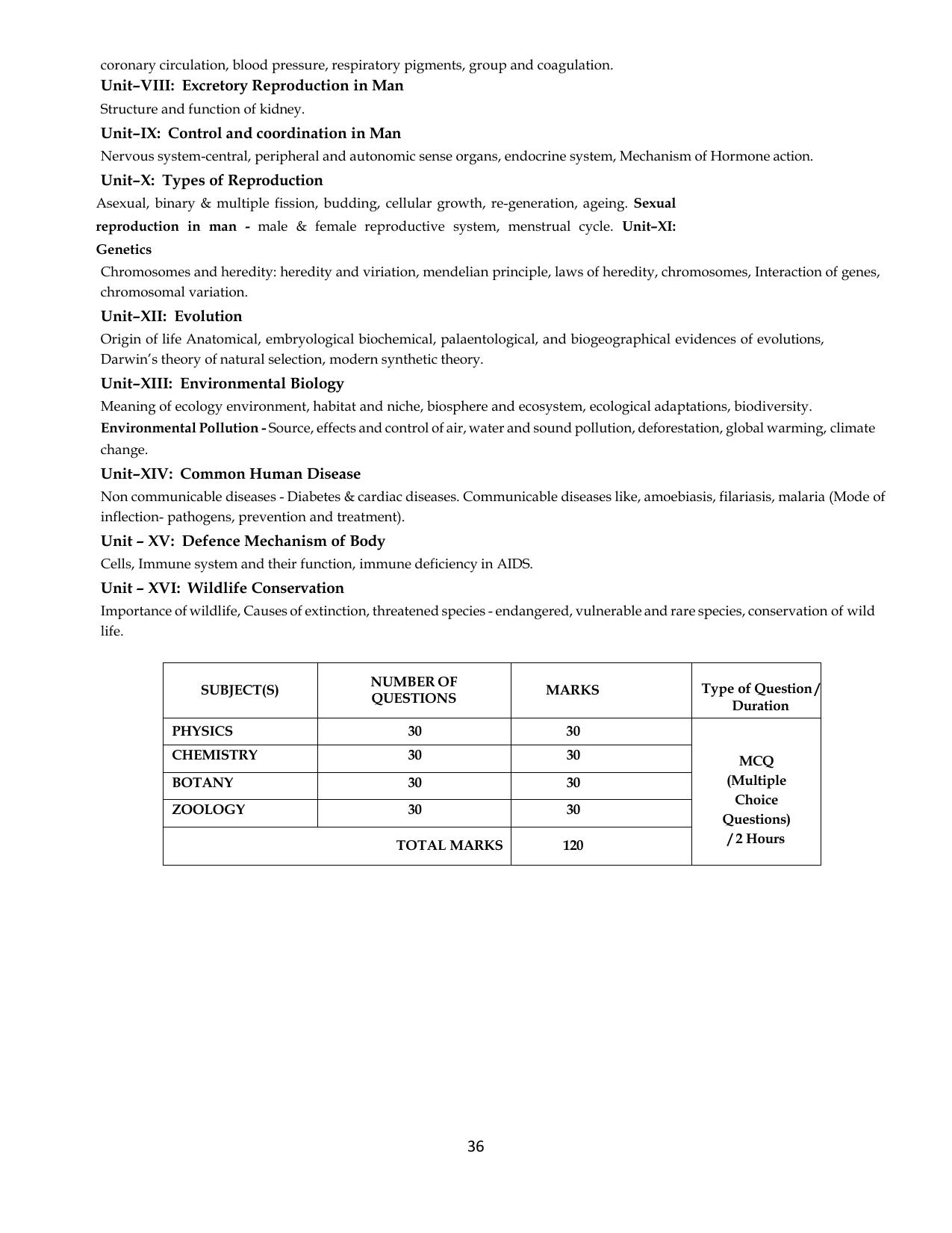
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration of exam | 2 hours |
| Mode of exam | Online |
| Number of questions | 120 |
| Maximum marks | 120 |
| Marking scheme | Correct answer: +1 Incorrect answer: -1 |
| Sections | Physics Chemistry Mathematics |
Paper Pattern
There will be multiple-choice questions.
– The number of questions will be 60 per each hour of exam
– SAAT exam duration is one hour.
– Each question shall have four probable answers with only one is correct answer, and the examinee shall have blackened only the correct circle with HB pencil or black/blue ballpoint pen
– Each correct answer shall carry four marks whereas each incorrect answer will lead to deduction of one mark. Each unanswered question will carry zero mark
– If more than one circle is darkened for one question, it will be treated as an incorrect answer and one mark will be deducted
– Each question is followed by answers, which have numbers A, B, C and D. Select the correct answer
– Then by using HB pencil or black/blue pen darken the circle bearing the correct answer in the answer sheet against the corresponding number of the question
How to download SAAT Syllabus?
To download the SAAT 2025 syllabus from indcareer.com, you can easily follow these steps:
Perform a search for “SAAT 2025 syllabus” to land on the relevant page.
On the page, locate and click on the link that provides the syllabus for the SAAT exam, which will open the document.
Once the document is open, find and click on the “Download PDF” link to save the syllabus of Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan Admission Test to your device.
It is crucial to thoroughly study all the topics mentioned in the syllabus for this common entrance exam. Additionally, solving SAAT previous year question papers will help you understand the types of questions expected in the exam conducted by SOA University, along with the chapter-wise weightage. To enhance your preparation, make sure to cover all the topics in the SAAT syllabus by referring to SAAT 2025 Preparation Books.
SAAT
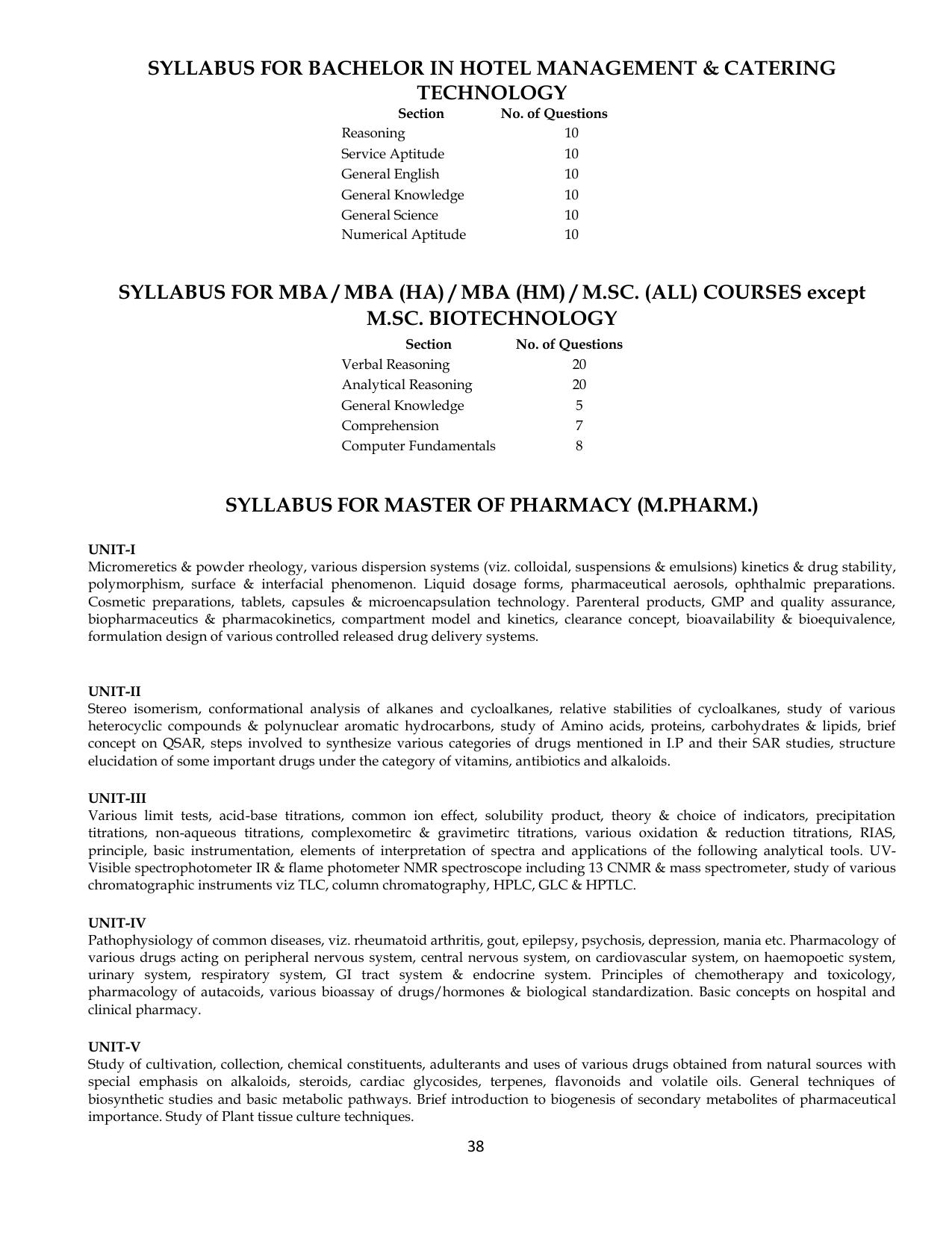
SAAT is a university-level common entrance exam conducted by Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (deemed to be University). The primary objective of this examination is to facilitate admissions to SOA University in various programs such as B.Tech, B.Pharm, B.Sc. Nursing, B.Sc. Agriculture, Lateral Entry to B.Tech, Lateral Entry B.Pharm, Lateral Entry BHMCT, MCA, BHMCT, MBA, MBA (HA), MBA (HM), M.Sc, M.Pharm, M.Tech, M.Sc. Agriculture, M.Sc. Nursing, P.B.B.Sc. Nursing, BA LLB, BBA LLB, LLB, BBA, BCA, LLM, Integrated M.Sc. Biotechnology (IB), and M.Sc. Biotechnology (M.Sc. BioTech.).
Quick Links
SAAT Syllabus – An Overview
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Name of Exam | SAAT |
| Full Form | Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan Admission Test |
| Study material Here | Syllabus of SAAT |
| Similar Exams | Common Entrance Exams |
| Official Body for Exam and Its Syllabus | SOA University |
| Full Name of Body | Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (deemed to be University) |
| Level of Examination | University Level |
| States of Region Where Institutes Accepting Exam Scores Are | Odisha |
| Exam and Syllabus Official Website | admission.soa.ac.in |
| Courses Where Admission Is Through This Exam | B.Tech, B.Pharm, B.Sc. Nursing, B.Sc. Agriculture, Lateral Entry to B.Tech, Lateral Entry B.Pharm, Lateral Entry BHMCT, MCA, BHMCT, MBA, MBA (HA), MBA (HM), M.Sc, M.Pharm, M.Tech, M.Sc. Agriculture, M.Sc. Nursing, P.B.B.Sc. Nursing, BA LLB, BBA LLB, LLB, BBA, BCA, LLM, Integrated M.Sc. Biotechnology (IB), M.Sc. Biotechnology (M.Sc. BioTech.) |
| Colleges Where Admission Is Through This Exam | SOA University |
