Contents
Panjab University Common Entrance Test (PUCET) entrance tests conducted by Panjab University, Chandigarh. The varsity at the onset of each academic session, which includes the PU Common Entrance Test for Under Graduate courses, PUCET and Common Entrance Test for Post Graduate courses, PUCET, apart from other department-wise entrance tests.
Mathematics
Unit I :
I. Sets and Functions
1. Sets : Sets and their representations, Empty set. Finite & Infinite sets, Equal sets. Subsets. Subsets of the set of real numbers especially intervals ( with notations ). Power set. Universal set. Venn diagrams, Union and Intersection of sets. Difference of sets. Complement of a set. Properties of complement sets.
2. Relations and Functions : Ordered pairs, Cartesian product of sets, Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the reals with itself ( upto R x R x R ). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain. Codomain and range of a relation. Function as a special kind of relation from one set to another. Pictorial representation of a function, domain, co – domain & range of a function. Real valued function of the real variable, domain and range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum and greatest integer functions with their graphs. Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions.
3. Trigonometric Functions : Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians & in degrees and conversion from one measure to another. Definition of trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle. Truth of the identity sin2 x + cos2 x = 1, for all x. Signs of trigonometric functions. Domain and range of trigonometric functions and their graphs. Expressing sin (x+y) and cos (x+y) in terms of sinx, siny, cosx & cosy. Deducing the identities like following :+

Identities related to sin 2x, cos2x, tan 2x, sin3x, cos3x and tan 3x. General solution of trigonometric equations of the type sin θ = sin α, cos θ = cos α and tan θ = tan α. Proof and simple applications of sine and cosine formulae.
II. Algebra
1. Principle of Mathematical Induction : Processes of the proof by induction, motivating the application of the method by looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications.
2. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations : Need for complex numbers, especially √−1, to be motivated by inability to solve every quadratic equation. Brief description of algebraic properties of complex numbers. Argand plane and polar representation of complex numbers. Statement of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, solution of quadratic equations in the complex number system.
3. Linear Inequalities : Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line. Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. Solution of system of linear inequalities in two variables.
4. Permutations and Combinations : Fundamental principle of counting, Factorial n. ( n! ) Permutation and combinations, derivation of formulae and their connections, simple applications.
5. Binomial Theorem : History, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices, Pascal’s triangle, general and middle term in binomial expansion, simple applications.
6. Sequences and Series : Sequence and Series. Arithmetic progression ( A. P. ). arithmetic mean ( A.M. ) Geometric progression G.P., general term of a G.P., sum of n terms of a G.P., geometric mean ( G.M. ), relation between A.M. and G.M. Sum to n terms of the special series
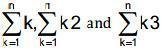
III. Coordinate Geometry
1. Straight Lines : Brief recall of 2D from earlier classes. Slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line : parallel to axes, point – slope form, slope – intercept form, two – point form, intercepts form and normal form. General equation of a line. Distance of a point from a line.
2. Conic Sections : Sections of a cone : circles, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, a point, a straight line and pair of intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section. Standard equations and simple properties of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. Standard equation of a circle.
3. Introduction to Three – dimensional Geometry : Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in three dimensions. Coordinates of a point. Distance between two points and section formula.
IV Calculus
1. Limits and Derivatives : Derivative introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometric meaning .
Definition of derivative, relate it to slope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions.
V. Mathematics Reasoning
Derivative introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometric meaning. Definition of derivative, relate it to slope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions.
V. Mathematics Reasoning
1. Mathematical Reasoning : Mathematically acceptable statements. Connecting words / phrases – consolidating the understanding of “if and only if ( necessary and sufficient ) condition”, “implies”, “and / or”, “implied by”, “and”, “or”, “there exists” and their use through variety of examples related to real life and Mathematics. Validating the statements involving the connecting words difference between contradiction, converse and contapositive.
VI. Statistics & Probability
1. Statistics : Measure of dispersion; mean deviation, variance and standard deviation of ungrouped / grouped data. Analysis of frequency distributions with equal means but different variances.
2. Probability : Random experiments : outcomes, sample spaces ( set representation ). Events : occurrence of events, ‘not’, ‘and’ and ‘or’ events, exhaustive events, mutually exclusive events Axiomatic ( set theoretic ) probability, connections with the theories of earlier classes, Probability of an event, probability of ‘not’, ‘and’ & ‘or’ events.
Unit – II Mathematics
I. Relations and Functions
1. Relations and Functions : Types of relations : reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations.
2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions : Definition, range, domain, principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions. Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
II. ALGEBRA
1. Matrices : Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication of matrices, simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non – commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of nonzero matrices whose product is the zero matrix ( restrict to square matrices of order 2 ). Concept of elementary row and column operation. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; ( Here all matrices will have real entries ).
2. Determinants : Determinant of a square matrix ( up to 3 x 3 matrices ), properties of determinants, minors, cofactors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle, Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables ( having unique solution ) using inverse of a matrix.
III. Calculus
1. Continuity and Differentiability : Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit function. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions and their derivative. Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems ( without proof ) and their geometric interpretations.
2. Applications of Derivatives : Application of derivatives : rate of change, increasing / decreasing functions, tangents & normals, approximation, maxima and minima ( first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool ). Simple problems ( that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real – life situations ).
3. Integrals : Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type.
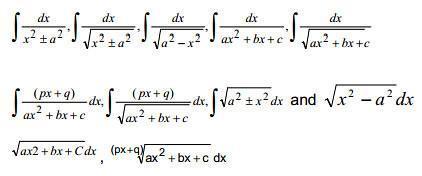
to be evaluated. Definite integrals as a limit of a sum, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus ( without proof ). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
4. Applications of the Integrals : Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, areas of circles / parabolas / ellipses ( in standard form only ), area between the two above said curves ( the region should be clearly identifiable ).
5. Differential Equations : Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of differential equation whose general solution is given. Solution of differential equations by method of separation variables, homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type :
dy / dx + py = q, where p and q are functions of x or constants.
+px = Q, where p and q are functions of y or constants.
IV Vectors and Three – Dimensional Geometry
1. Vectors : Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines / ratios of vectors. Types of vectors ( equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors ), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar ( dot ) product of vectors, projection of a vector on a line, Vector ( cross ) product of vectors.
2. Three – dimensional Geometry : Direction cosines / ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between ( i ) two lines, ( ii ) two planes. ( iii ) a line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
V. Linear Programming
1. Linear Programming : Introduction, definition of related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimisation, different types of linear programming ( L.P. ) problems, mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions, optional feasible solutions ( up to three non – trivial constrains ).
VI. Probability
1. Probability : Multiplication theorem on probability. Conditional probability, independent events, total probability, Baye’s theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution, mean and variance of haphazard variable. Repeated independent ( Bernoulli ) trials and Binomial distribution.
Physics
Unit I
1. Physical World and Measurement : Physics – scope and excitement; nature of physical laws; Physics, technology and society need for measurement : Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental and derived units. Length, mass and time measurements; accuracy and precision of measuring instruments; errors in measurement; significant figures. Dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional analysis and its applications.
2. Kinematics : Frame of reference. Motion in a straight line : Position – time graph, speed and velocity, Uniform and non – uniform motion, average speed and instantaneous velocity. Uniformly accelerated motion, velocity – time position – time graphs, relations for uniformly accelerated motion ( graphical treatment ). Elementary concepts of differentiation and integration for describing motion. Scalar and vector quantities, Position and displacement vectors, general vectors and notation; Equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; Addition and subtraction of vectors. Relative velocity.
Unit vector; Resolution of a vector in a plane – rectangular components. Motion in a plane. Cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration – projectile motion. Uniform circular motion.
3. Laws of Motion : Intuitive concept of force. Inertia, Newton’s first law of motion; momentum and Newton’s second law of motion; impulse; Newton’s third law of motion. Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications. Equilibrium of concurrent forces. Static and Kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction lubrication. Dynamics of uniform circular motion; Centripetal force, examples of circular motion ( vehicle on level circular road, vehicle on banked road ).
4. Work, Energy and Power : Work done by a constant force and a variable force; Kinetic energy, work energy theorem, power. Notion of Potential energy, potential energy of a spring, conservative forces; conservation of mechanical energy ( Kinetic and potential energies ), Non-conservative forces; Motion in vertical circle’ elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
5. Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body : Centre of mass of a two-particle system, momentum conservation and centre of mass motion. Centre of mass of a rigid body; centre of mass of uniform rod. Moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, laws of conservation of angular momentum and its applications.
Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions; Moment of inertia, radius of gyration. Values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects ( no derivation ). Statement of parallel and perpendicular axes theorems and their applications.
6. Gravitation : Keplar’s Laws of planetary motion. The universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth. Gravitational potential energy; gravitational potential. Escape velocity. Orbital velocity of a satellite. Geo – stationary satellites.
7. Properties of Bulk Matter : Elastic behaviour, Stress -strain relationship, Hooke’s Law, Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, shear, modulus of rigidity. Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal’s law and its applications ( hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes ). Effect of gravity on fluid pressure. Viscosity, Stokes’ law, terminal velocity, Reynold’s number, streamline and turbulent flow. Bernoulli’s theorem and its applications.
Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise. Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases, anomalous expansion of water, specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv – calorimetry; change of state – latent heat capacity.
Heat transfer – conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, Newton’s law of cooling. Qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wein’s displacement Law, Stefan’s law Green house effect.
8. Thermodynamics : Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature ( zeroth law of thermodynamics ), Heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics. Second law of thermodynamics : reversible and irreversible processes. Heat engines and refrigerators.
9. Behaviour of Prefect Gas and Kinetic Theory : Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases – assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic energy and temperature rms speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of equipartition of energy ( statement only ) and application to specific heats of gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro’s number.
10. Oscillations and Waves : Periodic motion – period, frequency, displacement as a function of time. Periodic function. Simple harmonic motion ( S.H.M ) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a spring – restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M.- Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum – derivation of expression for its time period; free, forced and damped oscillations ( qualitative ideas only ), resonance.
Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave motion. Displacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats, Doppler effect.
Unit – II
1. Electrostatics : Electric Charges; Conservation of charge, Coulomb’s law – force between two point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines; electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole’ torque on a dipole in uniform electric field. Electric flux, statement of Gauss’s theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell ( field inside and outside ).
Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarisation, capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor. Van de Graaff generator.
2. Current Electricity : Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm’s law, electrical resistance, V – I characteristics ( linear and non – linear ) electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity. Carbon resistors, colour code for carbon resistors; series and parallel combination of resistors; temperature dependence of resistance. Internal resistance of a cell, Potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel.
Kirchoff’s laws and simple applications. wheatstone bridge, metre bridge. Potentiometer – principle and its applications to measure potential difference and for comparing emf of two cells; measurement of internal resistance of a cell.
3. Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism : Concept of Magnetic field, Oersted’s experiment. Bio – Savart law and its applications to current carrying circular loop. Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron. Force on a current – carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel current -carrying conductors – definition of ampere.
Torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; moving coil galvanometer – its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter. Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment. Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron. Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole ( bar magnet ) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis. Torque on a magnetic dipole ( bar magnet ) in a uniform magnetic field; bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines; Earth’s magnetic field and magnetic elements. Para -, dia -and ferro – magnetic substances, with examples. Electromagnets and factor affecting their strengths. Permanent magnets.
4. Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating currents : Electromagnetic induction; Faraday’s law, induced emf and current; Lenz’s Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual inductance. Need for displacement current. Alternating currents, peak and rms value of alternating current / voltage; reactance and impedance; LC oscillations ( qualitative treatment only ), LCR series circuit, resonance; power in AC circuits, wattles current. AC generator and transformer.
5. Electromagnetic waves : Displacement Current, Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics ( qualitative ideas only ). Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic spectrum ( radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X rays, gamma rays ) including elementary facts about their uses.
6. Optics : Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula. Refraction of light, total internal reflection and its applications, optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens – maker’s formula. Magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact. Refraction and dispersion of light through a prism. Scattering of light – blue colour of the sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
Optical instruments : Human eye, image formation and accommodation, correction of eye defects ( myopia, Hypermetropia, presbyopia and astigmatism ) using lenses. Microscopes and astronomical telescopes ( reflecting and refracting ) and their magnifying powers. Wave optics; wave front and Huygens’ principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens’ principle.
Interference, Young’s double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light. Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum. Resolving power of microscopes and astronomical telescopes. Polarisation, plane polarised light; Brewster’s law, uses of plane polarised light and Polaroids.
7. Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation : Dual nature of radiation. Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard’s observations; Einstein’s photoelectric equation – particle nature of light. Matter waves – wave nature of particles, de Broglie relation. Davisson – Germer experiment.
8. Atoms & Nuclei : Alpha – particle scattering experiment; Rutherford’s model of atom; Bohr Model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, isotopes, isobars; isotones. Radioactivity – alpha, beta and gamma particles / rays and their properties; radioactive decay law. Mass – energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission and fusion.
9. Electronic Devices : Semiconductors; semiconductor diode – I- V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; I – V characteristics of LED, photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode; Zener diode as a voltage regulator. Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristics of a transistor; transistor as an amplifier ( common emitter configuration ) and oscillator. Logic gates ( OR, AND , NOT, NAND and NOR ). Transistor as a switch.
10. Communication Systems : Elements of a communication system ( block diagram only ); bandwidth of signals ( speech, TV and digital data ); bandwidth of transmission medium. Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the atmosphere, sky and space wave propagation. Need for modulation. Production and detection of an amplitude -modulated wave.
Chemistry
Unit – I
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry : General Introduction : Importance and scope of Chemistry. Nature of matter, laws of chemical combination. Dalton’s atomic theory : concept of elements, atoms and molecules. Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept and molar mass : percentage composition, empirical and molecular formula; chemical reactions, stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry.
2. Structure of Atom : Discovery of electron, proton and neutron; atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations, Rutherford’s model and its limitations. Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, De Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, concept of orbitals, quantum numbers, shapes of s, p, and d orbitals, rules for filling electrons in orbitals – Aufuau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule, electronic configuration of atoms, stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals.
3. Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties : Significance of classification, brief history of the development of periodic table, modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements- atomic radii, ionic radii. Ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, valence. Nomenclature of elements with atomic number greater than 100.
4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure : Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond : bond parameters. Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, covalent character of ionic bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry of covalent molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridisation, involving s, p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules, molecular ortibal; theory of homo nuclear diatomic molecules ( qualitative idea only ), hydrogen bond.
5. States of Matter : gases and liquids : Three states of matter. Intermolecular interactions, type of bonding, melting and boiling points. Role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law.
Charles law, Gay Lussac’s Law, Avogadro’s Law. Ideal behaviour, empirical derivation of gas equation, Avogadro’s number.Ideal gas equation. Derivation from ideal behaviour, liquefaction of gases, critical temperature, kinetic energy and molecular speeds ( elementary idea ). Liquid State – Vapour pressure, viscosity and surface tension ( qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations ).
6. Chemical Thermodynamics : Concepts Of System, types of systems, surroundings. Work, heat, energy, extensive and intensive properties, state functions. First law of thermodynamics – internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat, measurement of DU and DH, Hess’s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of : bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation. Phase transformation, ionization, and solution. Introduction of entropy as a state function, free energy change for spontaneous and non-spontaneous processes, criteria for equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics ( brief introduction ).
7. Equilibrium : Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of mass action, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium – Le Chatelier’s principle; ionic equilibrium -; ionisation of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionisation, concept of pH. Hydrolysis of salts ( elementary idea ). Buffer solutions, solubility product, common ion effect ( with illustrative examples ).
8. Redox Reactions : Concept of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number, balancing redox reactions, in terms of loss and gain of electrons and change in oxidation number, applications of redox reactions.
9. Hydrogen : Position of hydrogen in periodic table, occurrence, isotopes, preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen; hydrides – ionic, covalent and interstitial; physical and chemical properties of water, heavy water; hydrogen peroxide – preparation, properties and structure; hydrogen as a fuel.
10. s – Block Elements ( Alkali and Alkaline earth metals )
Group 1 and Group 2 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties ( such as ionisation enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii ), trends in chemical reactivity with oxygen, water, hydrogen and halogens; uses.
Preparation and properties of some important compounds : Sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate, biological importance of sodium and potassium. Calcium oxide and Calcium carbonate and their industrial uses, biological importance of Magnesium and Calcium.
11. Some p – Block Elements :
General Introduction to p – Block Elements
Group 13 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence. Variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous properties of first element of the group; Boron – physical and chemical properties, some important compounds : borax, boric acids, boron hydrides. Aluminium : uses, reactions with acids and alkalies uses.
Group 14 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous behaviour of first element, Carbon – catenation, allotropic forms, physical and chemical properties; uses of some important compounds : oxides
Important compounds of silicon and a few uses : silicon tetrachloride, silicones, silicates and zeolites their uses.
12. Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques : General introduction, method, qualitative and quantitative analysis, classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds. Electronic displacements in a covalent bond : inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyper conjugation. Homolytic and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond : free radicals, carbocations, carbanions; electrophiles and nucleophiles, types of organic reactions.
13. Hydrocarbons : Classification of Hydrocarbons
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons : Alkanes – Nomenclature, isomerism, conformations ( ethane only ), physical properties, chemical reactions including, free radical mechanism or halogenation, combustion and pyrolysis.
Alkenes – Nomenclature, structure of double bond ( ethane ) geometrical isomerism, physical properties, methods of preparation; chemical reactions : addition of hydrogen, halogen, water, hydrogen halides ( Markovnikov’s addition and peroxide effect ), ozonolysis, oxidation, mechanism of electrophilic addition.
Alkynes – Nomenclature, structure of triple bond ( ethyne ), physical properties. Mothods of preparation, chemical reactions; acidic character of alkynes, addition reaction of- hydrogen, halogens, hydrogen halides and water. Aromatic hydrocarbons: Introduction, IUPAC nomenclature; Benzene : resonance aromaticity; chemical properties : mechanism of electrophilic substitution. – nitration sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel Craft’s alkylation and acylation: directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene; carcinogenicity and toxicity.
14. Environmental Chemistry : Environmental pollution — air, water and soil pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere, smog, major atmospheric pollutants; acid rain, ozone and its reactions, effects of depletion of ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming -pollution due to industrial wastes; green chemistry as an alternative tool for reduction pollution, strategy for control of environmental Pollution.
Unit – II
1. Solid State : Classification of solids based on different binding forces: molecular, ionic, covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids ( elementary idea ), unit cell in two dimensional and three dimensional lattices, calculation of density of unit cell, packing in solids, voids, number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties. Band theory of metals, conductors, semiconductors and insulators and n & p type semiconductors.
2. Solutions : Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties – relative lowering of vapour pressure Raoult’s law, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass, van’t Hoff factor.
3. Electrochemistry : Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variations of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis and laws of electrolysis ( elementary idea ), dry cell – electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells; lead accumulator, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potetial, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, fuel cells; corrosion.
4. Chemical Kinetics : Rate of a reaction ( average and instantaneous ), factors a affecting rates of reaction; concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half life ( only for zero and first order reactions ); concept of collision theory ( elementary idea, no mathematical treatment ). Activation energy, Arrhenious equation.
5. Surface Chemistry : Adsorption – physisorption and chemisorption; factor affecting adsorption of gases on solids; catalysis : homogenous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity : enzyme catalysis; colloidal state: distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophilic, lyophobic, multimolecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation; emulsion – types of emulsions.
6. General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements : Principles and methods of extraction – concentration, oxidation, reduction electrolytic method and refining; occurrence and principles of extraction of aluminium, copper, zinc and Iron.
7. p -Block Elements :
Group 15 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties; nitrogen – preparation, properties and uses; compounds of nitrogen: preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid, oxides of nitrogen ( structure only ); Phosphorous -; allotropic forms; compounds of phosphorous : preparation and properties of phosphine, halides ( PCI3, PCI5 ) and oxoacids ( elementary idea only ).
Group 16 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; dioxygen : preparation, properties and uses; simple oxides; Ozone. Sulphur – allotropic forms; compounds of sulphur : preparation, properties and uses of sulphur dioxide; sulphuric acid: industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses, oxoacids of sulphur ( structures only ).
Group 17 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens : preparation, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds, oxoacids of halogens ( structures only )
Group 18 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration. Occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, uses.
8. d and f Block Elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals – metallic character, ionisation enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation. Preparation and properties of K2 Cr2 O7 and Kmno4.
Lanthanoids – electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanoid contraction.
Actinoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanoids.
9. Coordination Compounds : Coordination compounds -; Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding; isomerism, importance of coordination compounds ( in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological systems ).
10. Haloalkanes and Haloarenes :
Haloalkanes : Nomenclature, nature of C-X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions, optical rotation.
Haloarenes : Nature of C – X bond, substitution reactions ( directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds only ).
Uses and environmental effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT.
11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers :
Alcohols : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties ( of primary alcohols only ); identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses of methanol and ethanol.
Phenols : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophillic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
Ethers : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses.
12. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids :
Aldehydes and Ketones : Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, and mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
Carboxylic Acids : Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.’
13. Organic compounds containing Nitrogen
Amines : Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Cyanides and Isocyanides : will be mentioned at relevant places in context.
Diazonium salts : Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
14. Biomolecules :
Carbohydrates – Classification ( aldoses and ketoses ), monosaccahrides ( glucose and fructose ), oligosaccharides ( sucrose, lactose, maltose ), polysaccharides ( starch, cellulose, glycogen ); importance of carbohydrates.
Proteins -; Elementary idea of α – amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides proteins, structure of amines-primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures ( qualitative idea only ), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones – Elementary idea excluding structure. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
Vitamins – Classification and functions.
Nucleic Acids : DNA & RNA.
15. Polymers
Classification – natural and synthetics, methods of polymerisation ( addition and condensation ), copolymerisation. Some important polymers : natural and synthetic like polythene, nylon, polyesters, bakelite, rubber.
16. Chemistry in everyday life :
1. Chemicals in medicine – analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines.
2. Chemicals in food – preservatives, artificial sweetening agents.
3. Cleansing agents – soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
Biology
Unit- I
1. Diversity of Living Organisms :
What is living? biodiversity; need for classification; three domains of life; taxonomy & systematics; concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; binomial nomenclature; tools for study of taxonomy – museums, zorogical parks, herbaria, botanical gardens. Five kingdom classification; salient features and classification of Monera, Protista and Fungi into major groups : Lichens, Viruses and Viroids. Salient features and classification of plants into major groups – Algae, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnospermae and Angiospermae ( three to five salient and distinguising features and at least two examples of each category ); Angiosperms – classification up toclass, characteristic features and examples. Salient features and classification of animals non chordates up to phyla level and chordatesup to classes level ( three to five salient features and at least two examples ).
2. Structural Organization in Animals and Plants :
Morphology and modifications; tissues; anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: root, stem, leaf, inflorescence; cymose and racemose, flower, fruit and seed ( to be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus ).
Animal tissues; morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems ( digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive ) of an insect ( cockroach ). ( a brief account only ).
3. Cell Structure and Function ( 40 Periods )
Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles – structure and function; endomembrane system, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles ( ultrastructure and function ); nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus.
Chemical constituents of living cells : biomolecules, structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, enzymes, types, properties, enzyme action. Cell division : cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance.
strong>4. Plant Physiology :
Transport in plants; movement of water, gases and nutrients; cell to cell transport, Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; plant – water relations, Imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; long distance transport of water – Absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation; transpiration, opening and closing of stomata; Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients – Transport of food, phloem transport, mass flow hypothesis; diffusion of gases. Mineral nutrition : Essential minerals, macro and micronutrients and their role; deficiency symptoms; mineral toxicity; elementary idea of hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; nitrogen metabolism, nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation.
Photosynthesis : photosynthesis as a means of autotrophic nutrition; site of photosynthesis, pigments involved in photosynthesis ( elementary idea ); photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation; chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration; C3 and C4 pathways; factors affecting photosynthesis. Respiration : exchange of gases; cellular respiration – glycolysis, fermentation ( anaerobic ),
TCA cycle and electron transport system ( aerobic ); energy relations – number of ATP molecules generated; amphibolic pathways; respiratroy quotient. Plant growth and development : seed germination; phases of plant growth and plant growth rate; conditions of growth; differentiation, differentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of developmental processes in a plant cell; growth regulators – auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; seed dormancy; vernalisation; photoperiodism.
5. Human Physiology
Digestion and absorption : alimentary canal and digestive glands, role of digestive enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; calorific values of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; egestion; nutritional and digestive disorders – PEM, indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhoea.
Breathing and Respiration : Respiratory organs in animals ( recall only ); Respiratory system in humans; mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans – exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration, respiratory volume; disorders related to respiration – asthma, emphysema, occupational respiratory disorders.
Body fluids and circulation: composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; composition of lymph and its function; human circulatory system – Structure of human heart and blood vessels; cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG; double circulation; regulation of cardiac activity; disorders of circulatory system – hypertension, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, heart failure.
Excretory products and their elimination : modes of excretion – ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; human excretory system – structure and function; urine formation, osmoregulation; regulation of kidney function – renin – angiotensin, atrial natriuretic factor, ADH and diabetes insipidus; role of other organs in excretion; disorders – uraemia, renal failure, renal calculi, nephritis; dialysis and artificial kidney.
Locomotion and movement : types of movement – ciliary, flagellar, muscular; skeletal muscle – contractile proteins and muscle contraction; skeletal system and its functions; joints; disorders of muscular and skeletal system – myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscular dystrophy, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout.
Neural control and coordination: neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans – central nervous system; peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; generation and conduction of nerve impulse; reflex action; sensory perception; sense organs; elementary structure and function of eye and ear.
Chemical coordination and regulation : endocrine glands and hormones; human endocrine system – hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads; mechanism of hormone action ( elementary Idea ); role of hormones as messengers and regulators, hypo – and hyperactivity and related disorders; dwarfism, acromegaly, cretinism, goit, exophthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addision’s disease.
Note : Diseases related to all the human physiology systems ( to be taught in brief ).
Note : Diseases related to all the human physiology systems ( to be taught in brief ).
Unit – II
1. Reproduction
Reproduction in organisms : reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; asexual reproduction modes of reproduction – asexual and sexual reproduction; modes – binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plant : flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination – types, agencies and examples; outbreeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events -; development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation.
Human Reproduction : male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis -; spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation ( elementary idea ); parturition ( elementary idea ); lactation ( elementary idea ).
Reproductive health : need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases ( STD ); birth control – need and nethods, contraception and medical termination of pregnancy ( MTP ); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies -IVF, ZIFT, GIFT ( elementary idea for general awareness ).
2. Genetics and Evolution
Heredity and variation : Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; Sex determination – in humans, birds and honey bee; linkage and crossing over; sex linked inheritance – haemophilia, colour blindness; Mendelian disorder in humans -thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
Molecular basis of inheritance : search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation- Lac Operon; Genome and human geneome project; DNA fingerprinting. Evolution: origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution ( paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence ); Darwin’s contribution, modern synthetic theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution – variation ( mutation and recombination ) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy -Weinberg’s principle; adaptive radiation; human evolution.
3. Biology and Human Welfare :
Health and disease : pathogens; parasites causing human diseases ( malaria, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm ); Basic concepts of immunology – vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDs; Adolescene, drug and alcholol abuse.
Improvement in food production : Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification, Apiculature and Animal husbandry. Microbes in human welfare : In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
4. Biotechnology and its Application :
Principles and process of biotechnology : genetic engineering ( recombinant DNA technology ). application of biotechnology in health and agriculture : human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy; genetically modified organisms – Bt crops; transgenic animals; biosafety issues-biopiracy and patents.
5. Ecology and Environment 35 Periods
Organisms and environment : habitat and niche, population and ecological adaptations; population interactions – mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; population attributes- growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
Ecosystems : patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy; nutrient cycles ( carbon and phosphorous ); ecological succession; ecological services – carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release.
Biodiversity and its conservation : concept of biodiversity; patterns of biodiversity; importance of biodiversity; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, national parks and sanctuaries.
Environmental issues : Air pollution and its control; water pollution and its control; agrochemicals and their effects; solid waste management; radioactive waste management; greenhouse effect and global warning; ozone depletion; deforestation; any three case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues.
Biotechnology
Unit – I
1. Introduction to Biotechnology
Historical Perspectives; Production Strategies in Biotechnology; Quality Control; Product Safety; Good Manufacturing Practices; Good Laboratory Practices; Intellectual Property; Global market; Public Perception; Biotechnology in India and Global Trends.
2. Biomolecules
I. Building Blocks of Biomolecules – Structure and Dynamics; Building Blocks of Carbohydrates – Sugars and Their Derivatives; Building Blocks of Proteins – Amino Acids; Building Blocks of Lipids – Simple Fatty Acids, Sphingosine, Glycerol and Cholesterol; Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids -Nucleotides; Biochemical Transformations.
II : Structure and Function of Macromolecules 7 Marks ( 20 Periods ); Carbohydrates – The Energy Givers; Proteins – The Performers; Enzymes -The Catalysts; Lipids and Biomembranes -The Barriers; Nucleic Acids – The Managers.
III : Biochemical Techniques 5 Marks ( 10 Periods ); Techniques Based on Molecular Weight or Size; Techniques Based on Polarity or Charge; Techniques Based on Spectroscopy; Techniques Based on Solubility.
3. Cell and Development
I : The Basic Unit of Life; Cell Structure and Components; Tissues and Organs; Stem cells; Biodiversity; Organization of Life.
II : Cell Growth and Development; Cell Division; Cell Cycle; Cell Communication; Movement Nutrition; Gaseous Exchanges; Internal Transport.
Maintaining the Internal Environment; Reproduction; In Vitro Fertilization; Animal and Plant Development; Immune Response in Animals; Programmed Cell Death; Defense Mechanisms in Plants.
III : Cellular Techniques; Microscopy; Cell Sorting; Cell Fractionation; Cell Growth Determination.
4. Genetics and Molecular Biology
I : Principles of Genetics; Historical Perspective; Multiple Alleles; Linkage and Crossing Over; Genetic Mapping; Gene Interaction; Sex-Linked Inheritance; Extranuclear Inheritance; Quantitative Inheritance; Genes at Population Level; Discovery of DNA as Genetic Material; Mutations; DNA Repair; Genetic Disorders.
II : Genome Function; Genome Organization; DNA Replication; Fine Structure of Genes; From Gene to Protein; Transcription – The Basic Process; Genetic Code; Translation; Regulation of Gene Expression.
III : Genetical Techniques; Chromosomal Techniques; Mutagenic Techniques; Recombination in Bacteria; Breeding Methods in Plants; Pedigree Analysis in Humans.
Unit – II
1. Protein and Gene Manipulation Marks 40 ( 100 Periods )
I : Recombinant DNA Technology 15 Marks ( 40 Periods ); Introduction; Tool of rDNA Technology; Making rDNA; Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Host Cells; Identification of Recombinants; Polymerase Chain Reaction ( PCR ); Hybridization Techniques; DNA Library; DNA Sequencing; Site-directed Mutagenesis.
II : Protein Structure and Engineering 15 Marks ( 35 Periods ); Introduction to the World of Proteins; 3-D Shape of Proteins; Structure-Function Relationship in Proteins; Purification of Proteins; Characterization of Proteins; Protein Based Products; Designing Proteins ( Protein Engineering ).
III : Genomics and Bioinformatics 10 Marks ( 25 Periods ); Introduction; Genome Sequencing Projects; Gene Prediction and Counting; Genome Similarity, SNPs and Comparative Genomics; Functional Genomics; Proteomics; History of Bioinformatics; Sequences and Nomenclature; Information Sources; Analysis using Bioinformatics Tools.
2. Cell Culture and Genetic Manipulation 30 Marks ( 80 Periods )
I : Microbial Culture and Applications 10 Marks ( 26 Periods ) : Introduction; Microbial Culture Techniques; Measurement and Kinetics of Microbial Growth; Scale up of Microbial Process; Isolation of Microbial Products; Strain isolation and Improvement; Applications of Microbial Culture Technology; Biosafety Issues in Microbial Technology.
II : Plant Cell Culture and Applications 10 Marks ( 27 Periods ) : Introduction; Cell and Tissue Culture Techniques; Applications of Cell and Tissue Culture; Gene Transfer Methods in Plants; Transgenic Plants with Beneficial Traits; Biosafety in Plant Genetic Engineering.
III : Animal Cell Culture and Applications 10 Marks ( 27 Periods ) : Introduction; Animal Cell Culture Techniques; Characterisation of Cell Lines; Methods of Gene Delivery into Cells; Scale-up of Animal Culture Process; Applications of Animal Cell Culture; Stem Cell Technology; Tissue Engineering.
Computer Science
Unit – I
1. Computer Fundamentals
Evolution of computers; Basics of computer system and its operation : Functional Components and their interconnections, concept of Booting.
Software Concepts :
Types of Software – System Software, Utility Software and Application Software;
System Software : Operating System, Compiler, Interpreter and Assembler;
Operating System : Need for operating system, Functions of Operating System ( Processor Management, Memory Management, File Management and Device Management ), Types of operating system – Class XI ( Theory ) Interactive ( GUI based ), Real Time and Distributed; Commonly used operating systems : UNIX, LINUX, Windows, Solaris, BOSS ( Bharat Operating System Solutions ); Mobile OS – Android, Symbian. Illustration and practice of the following tasks using any one of the above Operating Systems :
- Opening / Closing Windows
- Creating / Moving / Deleting Files / Folders
- Renaming Files / Folders
- Switching between Tasks
Utility Software : Anti Virus, File Management tools, Compression tools and Disk Management tools ( Disk Cleanup, Disk Defragmenter, Backup ).
Application software : Office Tools – Word Processor, Presentation Tool, Spreadsheet Package, Database Management System; Domain specific tools- School Management System, Inventory Management System, Payroll System, Financial Accounting, Hotel Management, Reservation System and Weather Forecasting System.
Number System : Binary, Octal, Decimal, Hexadecimal and conversion amongst these number systems.
Internal Storage encoding of Characters : ASCII, ISCII ( Indian scripts Standard Code for Information Interchange ), and UNICODE ( for multilingual computing )
Microprocessor : Basic concepts, Clock speed ( MHz, GHz ), 16 bit, 32 bit, 64 bit processors, 128 bit processors; Types – CISC Processores ( Complex Instruction set computing ), RISC Processors ( Reduced Instruction set computing ), and EPIC ( Explicitly parallel Instruction computing ).
Memory Concepts : Units : Byte, Kilo Byte, Mega Byte, Giga Byte, Tera Byte, Peta Byte, Exa Byte, Zetta Byte, Yotta Byte.
Primary Memory : Cache, RAM, ROM
Secondary Memory : Fixed and Removable Storage – Hard Disk Drive, CD / DVD Drive, Pen Drive, Blue Ray Disk
Input Output Ports / Connections : Serial, Parallel and Universal Serial Bus, PS-2 port, Infrared port, Bluetooth, Firewire.
Note : Exploring inside computer system in the computer lab class.
2 : Introduction to C++
Getting Started : C++ character set, C++ Tokens ( Identifiers, Keywords, Constants, Operators ), Structure of a C++ Program ( include files, main function ); Header files – iostream.h, iomanip.h; cout, cin; Use of I/O operators ( << and >> ), Use of endl and setw(), Cascading of I/O operators, Error Messages; Use of editor, basic commands of editor, compilation, linking and execution;
Data Types, Variables and Constants : Concept of Data types; Built-in Data types : char, int, float and double; Constants : Integer Constants, Character Constants ( Backslash character constants – n, t ), Floating Point Constants, String Constants; Access modifier : const; Variables of built-in data types, Declaration / Initialisation of variables, Assignment statement; Type modifier : signed, unsigned, long;
Operators and Expressions : Operators : Arithmetic operators ( -,+,*,/,% ), Unary operator (-), Increment (++) and Decrement (–) Operators, Relation operator ( >,>=,<,<=,= =,!= ), Logical operators (!, &&,||), Conditional operator : <condition>? <if true>:<if false>; Precedence of Operators; Automatic type conversion in expressions, Type casting; C++ shorthands ( +=, -=, *=,/=, %= ).
3 : Programming Methodology
General Concepts; Modular approach; Clarity and Simplicity of Expressions, Use of proper Names for identifiers, Comments, Indentation; Documentation and Program Maintenance; Running and Debugging programs, Syntax Errors, Run-Time Errors, Logical Errors.
Problem Solving Methodologies : Understanding of the problem, Identifying minimum number of inputs required for output, Writing code to optimizing execution time and memory storage, step by step solution for the problem, breaking down solution into simple steps, Identification of arithmetic and logical operations required for solution,
Control Structure : Conditional control and looping ( finite and infinite ).
4 : Programming in C++
Flow of control :
Conditional statements : if-else, Nested if, switch..case..default, use of conditional operator, Nested switch..case, break statement ( to be used in switch..case only );
Loops : while, do- while , for and Nested loops.
Introduction to user-defined function and its requirements. Defining a function; function prototype, Invoking / calling a function, passing arguments to function, specifying argument data types, default argument, constant argument, call by value, call by reference, returning values from a function, calling functions with arrays, scope rules of functions and variables local and global variables. Relating the Parameters and return type concepts in built-in functions.
Structured Data Type :
Arrays : Introductory to Array and its advantages.
One Dimensional Array : Declaration / initialisation of One-dimensional array, Inputting array elements, Accessing array elements, Manipulation of Array elements ( sum of elements, product of elements, average of elements, linear search, finding maximum / minimum value ) Declaration / Initialization of a String, string manipulations ( counting vowels / consonants / digits / special characters, case conversion, reversing a string, reversing each word of a string ).
Two-dimensional Array : Declaration / initialisation of a two-dimensional array, inputting array elements Accessing array elements, Manipulation of Array elements ( sum of row element, column elements, diagonal elements, finding maximum / minimum values ).
User-defined Data Types : Introduction to user defined data types.
Structure : Defining a Structure ( Keyword Structure ), Declaring structure variables, Accessing structure elements, Passing structure to Functions as value and reference argument / parameter, Function returning structure, Array of structures, passing an array of structure as an argument / a parameter to a function Defining a symbol name using typedef keyword and defining a macro using #define directive.
UNIT- II
1. Programming in C++
Object Oriented Programming : Concept of Object Oriented Programming – Data hiding, Data encapsulation, Class and Object, Abstract class and Concrete class, Polymorphism ( Implementation of polymorphism using Function overloading as an example in C++ ); Inheritance, Advantages of Object Oriented Programming over earlier programming methodologies,
Implementation of Object Oriented Programming concepts in C++ : Definition of a class, Members of a class – Data Members and Member Functions ( methods ), Using Private and Public visibility modes, default visibility mode ( private ); Member function definition : inside class definition and outside class definition using scope resolution operator (::); Declaration of objects as instances of a class; accessing members from object(s), Objects as function arguments – pass by value and pass by reference;
Constructor and Destructor : Constructor: Special Characteristics, Declaration and Definition of a constructor, Default Constructor, Overloaded Constructors, Copy Constructor, Constructor with default arguments; Destructor: Special Characteristics, Declaration and definition of destructor;
Inheritance ( Extending Classes ) : Concept of Inheritance, Base Class, Derived Class, Defining derived classes, protected visibility mode; Single level inheritance, Multilevel inheritance and Multiple inheritance, Privately derived, Publicly derived and Protectedly derived class, accessibility of members from objects and within derived class(es);
Data File Handling : Need for a data file, Types of data files – Text file and Binary file;
Text File : Basic file operations on text file: Creating/Writing text into file, Reading and manipulation of text from an already existing text File ( accessing sequentially );
Binary File : Creation of file, Writing data into file, Searching for required data from file, Appending data to a file, Insertion of data in sorted file, Deletion of data from file, Modification of data in a file; Implementation of above mentioned data file handling in C++;
Components of C++ to be used with file handling : Header file: fstream.h; ifstream, ofstream, fstream classes; Opening a text file in in, out, and app modes; Using cascading operators for writing text to the file and reading text from the file; open(), get(), put(), getline() and close() functions; Detecting end-of-file ( with or without using eof() function ); Opening a binary file using in, out, and app modes; open(), read(), write() and close() functions; Detecting end-of-file ( with or without using eof() function ); tellg(), tellp(), seekg(), seekp() functions.
Pointers : Declaration and Initialization of Pointers; Dynamic memory allocation / deallocation operators: new, delete; Pointers and Arrays : Array of Pointers, Pointer to an array ( 1 dimensional array ), Function returning a pointer, Reference variables and use of alias; Function call by reference. Pointer to structures: Deference operator: *, ->; self referencial structures;
2 : Data Structures
Introduction to data structure, primitive and non-primitive data structure, linear and non-linear structure, static and dynamic data structure.
Arrays : One and two Dimensional arrays: Sequential allocation and address calculation;
One dimensional array : Traversal, Searching ( Linear, Binary Search ), Insertion of an element in an array, deletion of an element from an array, Sorting ( Insertion, Selection )
Two-dimensional arrays : Traversal, Finding sum / difference of two NxM arrays containing numeric values, Interchanging Row and Column elements in a two dimensional array;
Stack ( Array and Linked implementation of Stack ) : Introduction to stock ( LIFO _ Last in First Out Operations )
Operations on Stack ( PUSH and POP ) and its Implementation in C++, Converting expressions from INFIX to POSTFIX notation and evaluation of Postfix expression;
Queue : ( Circular Array and Linked Implementation ) :
Introduction to Queue ( FIFO – First in First out operations )
Operations on Queue ( Insert and Delete ) and its Implementation in C++.
3 : Databases Management System and SQL :
Database Concepts : Introduction to data base concepts and its need.
Relational data model : Concept of domain, tuple, relation, key, primary key, alternate key, candidate key;
Relational algebra : Selection, Projection, Union and Cartesian product;
Structured Query Language :
General Concepts : Advantages of using SQL, Data Definition Language and Data Manipulation Language;
Data types : NUMBER / DECIMAL, CHARACTER / VARCHAR / VARCHAR2, DATE;
SQL commands :
CREATE TABLE, DROP TABLE, ALTER TABLE, UPDATE…SET…, INSERT, DELETE; SELECT, DISTINCT, FROM, WHERE, IN, BETWEEN, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY; SQL functions: SUM, AVG, COUNT, MAX and MIN; Obtaining results ( SELECT query ) from 2 tables using equi-join, Cartesian Product and Union Note : Implementation of the above mentioned commands could be done on any SQL supported software on one or two tables.
4 : Boolean Algebra
Role of Logical Operations in Computing. Binary-valued Quantities, Logical Variable, Logical Constant and Logical Operators : AND, OR, NOT; Truth Tables; Closure Property, Commutative Law, Associative Law, Identity law, Inverse law, Principle of Duality, Idem potent Law, Distributive Law, Absorption Law, Involution law, DeMorgan’s Law and their applications; Obtaining Sum of Product ( SOP ) and Product of Sum ( POS ) form from the Truth Table, Reducing Boolean Expression ( SOP and POS ) to its minimal form, Use of Karnaugh Map for minimization of Boolean expressions ( up to 4 variables );
Application of Computing Logic : Building up logic circuits using basic Logic Gates ( NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOT ) Use of Boolean operators ( NOT, AND, OR ) in SQL SELECT statements Use of Boolean operators ( AND, OR ) in search engine queries.
5 : Networking and Open Source Software
Communication Technologies
Evolution of Networking : ARPANET, www, Internet, Interspace Different ways of sending data across the network with reference to switching techniques ( Circuit, Message and Packet switching ).
Data Communication terminologies : Concept of Channel and Data transfer rate ( bps, kbps, Mbps, Gbps, Tbps ).
Transmission media : Twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, optical fiber, infrared, radio link, microwave link and satellite link.
Network devices : Modem RJ11and RJ45 connectors, Ethernet Card, Hub, Switch, Gateway
Network Topologies and types : Bus, Star, Tree; PAN, LAN, WAN, MAN
Network Protocol : TCP / IP, File Transfer Protocol ( FTP ), PPP, Remote Login ( Telnet ), Internet Wireless / Mobile Communication protocol such as GSM, CDMA, GPRS, WLL, Mobile Telecommunication Technologies : 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G Electronic mail protocols such as SMTP, POP3 Protocols for Chat and Video Conferencing VOIP Wireless protocols such as Wi-Fi and WiMax.
Network Security Concepts : Threats and prevention from Viruses, Worms, Trojan horse, Spams Use of Cookies, Protection using Firewall; India IT Act, Cyber Law, Cyber Crimes, IPR issues, Hacking.
WebServices : WWW, Hyper Text Markup Language ( HTML ), eXtensible Markup Language ( XML ); Hyper Text Transfer Protocol ( HTTP ); Domain Names; URL; Protocol Address; Website, Web browser, Web Servers; Web Hosting, Web Scripting -; Client side ( VB Script, Java Script, PHP ) and Server side ( ASP, JSP, PHP ), Web 2.0 ( for social networking ).
Open Standards : Introduction to open standards and its advantage in development of inter-operable environment.
Open Source Concepts : Proprietory and Open Source Software, Freeware, Shareware, FLOSS / FOSS, GNU,FSF, OSI, W3C
Cloud Computing :
Characteristics, layers-client, Application, platform and infrastructure, Deployment models-Private cloud, Public cloud, Community cloud and hybrid cloud, Issues-Privacy, Compliance, Security, Sustainability and abuse.
PU CET
PU CET is a university-level common entrance exam conducted by Panjab University. The primary objective of this exam is to facilitate admissions to Panjab University for B.Sc. (Hons.) and B. Pharmacy programs.
Quick Link
PU CET Syllabus – An Overview
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Exam | PU CET UG |
| Full Name of Exam | Panjab University Common Entrance Test Under Graduate |
| Details or Event Here | Syllabusn of PU CET |
| Similar Exams and Their Registration | Common Entrance Exams |
| States or Regions of Score Accepting Colleges | Chandigarh |
| Official Body That Issues Application Form | PU |
| Full Form of Organization | Panjab University |
| Official Website for Registration Details | cetug.puchd.ac.in |
| Programs Where Admission Is Through This Exam | B.Sc. (Hons.), B. Pharmacy |
| Colleges and Universities Where Admission Is Through This Exam | Panjab University |
